
AC T04379
XX
ID T04379
XX
DT 14.03.2001 (created); dkl.
DT 29.11.2005 (updated); mkl.
CO Copyright (C), QIAGEN.
XX
FA MEDEA-A (MED)
XX
SY CG1775; Med; MEDEA-A; MEDEA-A (MED)(d).
XX
OS fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster
OC eukaryota; animalia; metazoa; arthropoda; insecta; diptera; drosophiloidea; drosophilidae
XX
GE G002363 Med.
XX
HO SMAD-4 human T04292 [1] [2]; SMAD-4 mouse [1] [1] [2].
XX
CL C0041; SMAD.
XX
SZ 771 AA; 81.6 kDa (cDNA) (calc.).
XX
SQ MGGGSGACPPAHMYGAVAPQDIIVRDMVQMPPPPSNAPTSADACLSIVHSLMCHRQGGES
SQ EGFAKRAIESLVKKLKEKRDELDSLITAITTNGAHPSKCVTIQRTLDGRLQVAGRKGFPH
SQ VIYARIWRWPDLHKNELKHVKYCAFAFDLKCDSVCVNPYHYERVVSPGIDLSGLSLQSGP
SQ SRLVKDEYSAGPLVGSMDIDGNDIGTIQHHPTQMVGPGGYGYPQGPSEYVGDANPMSAMF
SQ PTGRTIPKIEPQDGVAGSRGSWMVPPPPRLGQPPQQQQQQPQQQTPQPTQQQQAQSQAAA
SQ HSLPVPHGMPGMPGPMNPGPVMAPPPPPQQAQNPQGNGVHHTQANSPTDPASALAMQQQQ
SQ QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQSGGVPNGSVNAGGGAAAGGQYYGQPPPVSQMQGAGGGGTSVAPS
SQ VHAQQNGYVSQPGSAGSAPVGGGGVFGTAQPTPQQPQQPPTGVQANTGSAGAQAGAGGGA
SQ AGTWTGPNTLTYTQSMQPPDPRSLPGGFWNSSLSGDLGSPQQTPPQQQQQQQQPRLLSRQ
SQ PPPEYWCSIAYFELDTQVGETFKVPSAKPNVIIDGYVDPSGGNRFCLGALSNVHRTEQSE
SQ RARLHIGKGVQLDLRGEGDVWLRCLSDNSVFVQSYYLDREAGRTPGDAVHKIYPAACIKV
SQ FDLRQCHQQMHSLATNAQAAAAAQAAAVAGVANQQMGGGGRSMTAAAGIGVDDLRRLCIL
SQ RLSFVKGWGPDYPRQSIKETPCWIEVHLHRALQLLDEVLHAMPIDGPRAAA
XX
SC translated from EMBL #AF027729
XX
FT 1 48  N-terminus [2].
FT 46 170
N-terminus [2].
FT 46 170  PS51075; MH1.
FT 49 177
PS51075; MH1.
FT 49 177  MH1 domain [2].
FT 59 168
MH1 domain [2].
FT 59 168  SM00523; dwAneu5.
FT 61 165
SM00523; dwAneu5.
FT 61 165  PF03165; MH1 domain.
FT 73 77
PF03165; MH1 domain.
FT 73 77  defective Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) [5].
FT 178 540
defective Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) [5].
FT 178 540  Linker region [2].
FT 540 751
Linker region [2].
FT 540 751  PF03166; MH2 domain.
FT 541 771
PF03166; MH2 domain.
FT 541 771  MH2 domain [2].
FT 544 749
MH2 domain [2].
FT 544 749  SM00524; DWB.
FT 546 771
SM00524; DWB.
FT 546 771  PS51076; MH2.
PS51076; MH2.
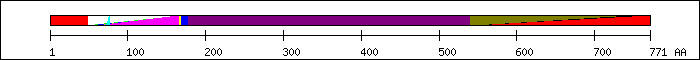 XX
SF in comparison to the Smad-4 homologs and Mad, MEDEA-A (MED) is lacking the SSXS motif at the C-terminus [3];
SF in MEDEA-A (MED)-B exon 4 is missing (73 bps in the linker region) [3];
SF the presence or absence of alternative exon 4 does not affect MEDEA-A (MED) binding activity [3];
SF the first encoded methionine is used as the translational start, although a good Drosophila consensus translational start does not occur until the third methionine, M27 [2];
SF in conflict to SPTREMBL # O61458, here M27 is used as translational start site resulting in an ORF of 745 AAs [1] [4];
SF in conflict to 771 AAs [2];
SF given start and end positions of domains and regions of the protein recruited from reference_no 15907 are in conflict to [1] [3];
SF defective NLS (Nuclear Localization Signal) in comparison to R-Smads [5];
SF after phosphorylation of MAD at the C-terminus it interacts physically with MEDEA-A (MED) [2];
SF MH2 domain of MEDEA-A (MED) is essential for the formation of productive heteromeric MAD/MEDEA-A (MED) complexes, whereas the MH1 domain is not [2];
SF entrance into the nucleus requires physical association with phosphorylated MAD [2];
XX
CP embryo: ubiquitously expressed, but at varying levels, during embryonic development [2]; stage 4: widespread transcript localization, maternal contribution [2]; stage7: strong expression in mesoderm and head region [2]; stage 14: throughout ectoderm, endoderm, central nervous system [2]; stage 16: low levels in second midgut constriction, higher levels in central nervous system [2]; [2].
XX
FF involved in dpp-signaling, acts downstream of TKV (Thick vein receptor)-receptor (receptor-type I) [1];
FF required for all dpp-dependent signaling in embryonic dorsal-ventral patterning [1] [2];
FF in knock-out studies, null embryos bore fully ventralized cuticles that were indistinguishable from dpp null embryos [2];
FF Embryos with one Medea+ chromosome had a weaker phenotype, indicating that patterning is sensitive to different levels of Medea function [2];
XX
BS R10035.
BS R10036.
BS R10100.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000019017.
DR EMBL: AF019754; AF019754.
DR EMBL: AF027729; AF027729.
DR UniProtKB: O62609; O62609.
DR UniProtKB: Q9U010; Q9U010.
DR FLYBASE: FBgn0011655.
XX
RN [1]; RE0015899.
RX PUBMED: 9502722.
RA Hudson J. B., Podos S. D., Keith K., Simpson S. L., Ferguson E. L.
RT The Drosophila Medea gene is required downstream of dpp and encodes a functional homolog of human Smad4.
RL Development 125:1407-1420 (1998).
RN [2]; RE0015907.
RX PUBMED: 9502724.
RA Wisotzkey R. G., Mehra A., Sutherland D. J., Dobens L. L., Liu X., Dohrmann C., Attisano L., Raftery L. A.
RT Medea is a Drosophila Smad4 homolog that is differentially required to potentiate DPP responses.
RL Development 125:1433-1445 (1998).
RN [3]; RE0015913.
RX PUBMED: 9694800.
RA Xu X., Yin Z., Hudson J. B., Ferguson E. L., Frasch M.
RT Smad proteins act in combination with synergistic and antagonistic regulators to target Dpp responses to the Drosophila mesoderm.
RL Genes Dev. 12:2354-2370 (1998).
RN [4]; RE0015915.
RX PUBMED: 9693372.
RA Inoue H., Imamura T., Ishidou Y., Takase M., Udagawa Y., Oka Y., Tsuneizumi K., Tabata T., Miyazono K., Kawabata M.
RT Interplay of signal mediators of decapentaplegic (Dpp): molecular characterization of mothers against dpp, Medea, and daughters against dpp.
RL Mol. Biol. Cell 9:2145-2156 (1998).
RN [5]; RE0016203.
RX PUBMED: 10884415.
RA Xiao Z., Liu X., Henis Y. I., Lodish H. F.
RT A distinct nuclear localization signal in the N terminus of Smad 3 determines its ligand-induced nuclear translocation.
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:7853-7858 (2000).
RN [6]; RE0022036.
RX PUBMED: 10370243.
RA Zhang Y., Derynck R.
RT Regulation of Smad signalling by protein associations and signalling crosstalk
RL Trends Cell Biol. 9:274-279 (1999).
RN [7]; RE0022065.
RX PUBMED: 10712925.
RA Attisano L., Wrana J. L.
RT Smads as transcriptional co-modulators
RL Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:235-243 (2000).
RN [8]; RE0022072.
RX PUBMED: 10831835.
RA Zimmerman C. M., Padgett R. W.
RT Transforming growth factor beta signaling mediators and modulators
RL Gene 249:17-30 (2000).
XX
//
XX
SF in comparison to the Smad-4 homologs and Mad, MEDEA-A (MED) is lacking the SSXS motif at the C-terminus [3];
SF in MEDEA-A (MED)-B exon 4 is missing (73 bps in the linker region) [3];
SF the presence or absence of alternative exon 4 does not affect MEDEA-A (MED) binding activity [3];
SF the first encoded methionine is used as the translational start, although a good Drosophila consensus translational start does not occur until the third methionine, M27 [2];
SF in conflict to SPTREMBL # O61458, here M27 is used as translational start site resulting in an ORF of 745 AAs [1] [4];
SF in conflict to 771 AAs [2];
SF given start and end positions of domains and regions of the protein recruited from reference_no 15907 are in conflict to [1] [3];
SF defective NLS (Nuclear Localization Signal) in comparison to R-Smads [5];
SF after phosphorylation of MAD at the C-terminus it interacts physically with MEDEA-A (MED) [2];
SF MH2 domain of MEDEA-A (MED) is essential for the formation of productive heteromeric MAD/MEDEA-A (MED) complexes, whereas the MH1 domain is not [2];
SF entrance into the nucleus requires physical association with phosphorylated MAD [2];
XX
CP embryo: ubiquitously expressed, but at varying levels, during embryonic development [2]; stage 4: widespread transcript localization, maternal contribution [2]; stage7: strong expression in mesoderm and head region [2]; stage 14: throughout ectoderm, endoderm, central nervous system [2]; stage 16: low levels in second midgut constriction, higher levels in central nervous system [2]; [2].
XX
FF involved in dpp-signaling, acts downstream of TKV (Thick vein receptor)-receptor (receptor-type I) [1];
FF required for all dpp-dependent signaling in embryonic dorsal-ventral patterning [1] [2];
FF in knock-out studies, null embryos bore fully ventralized cuticles that were indistinguishable from dpp null embryos [2];
FF Embryos with one Medea+ chromosome had a weaker phenotype, indicating that patterning is sensitive to different levels of Medea function [2];
XX
BS R10035.
BS R10036.
BS R10100.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000019017.
DR EMBL: AF019754; AF019754.
DR EMBL: AF027729; AF027729.
DR UniProtKB: O62609; O62609.
DR UniProtKB: Q9U010; Q9U010.
DR FLYBASE: FBgn0011655.
XX
RN [1]; RE0015899.
RX PUBMED: 9502722.
RA Hudson J. B., Podos S. D., Keith K., Simpson S. L., Ferguson E. L.
RT The Drosophila Medea gene is required downstream of dpp and encodes a functional homolog of human Smad4.
RL Development 125:1407-1420 (1998).
RN [2]; RE0015907.
RX PUBMED: 9502724.
RA Wisotzkey R. G., Mehra A., Sutherland D. J., Dobens L. L., Liu X., Dohrmann C., Attisano L., Raftery L. A.
RT Medea is a Drosophila Smad4 homolog that is differentially required to potentiate DPP responses.
RL Development 125:1433-1445 (1998).
RN [3]; RE0015913.
RX PUBMED: 9694800.
RA Xu X., Yin Z., Hudson J. B., Ferguson E. L., Frasch M.
RT Smad proteins act in combination with synergistic and antagonistic regulators to target Dpp responses to the Drosophila mesoderm.
RL Genes Dev. 12:2354-2370 (1998).
RN [4]; RE0015915.
RX PUBMED: 9693372.
RA Inoue H., Imamura T., Ishidou Y., Takase M., Udagawa Y., Oka Y., Tsuneizumi K., Tabata T., Miyazono K., Kawabata M.
RT Interplay of signal mediators of decapentaplegic (Dpp): molecular characterization of mothers against dpp, Medea, and daughters against dpp.
RL Mol. Biol. Cell 9:2145-2156 (1998).
RN [5]; RE0016203.
RX PUBMED: 10884415.
RA Xiao Z., Liu X., Henis Y. I., Lodish H. F.
RT A distinct nuclear localization signal in the N terminus of Smad 3 determines its ligand-induced nuclear translocation.
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:7853-7858 (2000).
RN [6]; RE0022036.
RX PUBMED: 10370243.
RA Zhang Y., Derynck R.
RT Regulation of Smad signalling by protein associations and signalling crosstalk
RL Trends Cell Biol. 9:274-279 (1999).
RN [7]; RE0022065.
RX PUBMED: 10712925.
RA Attisano L., Wrana J. L.
RT Smads as transcriptional co-modulators
RL Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:235-243 (2000).
RN [8]; RE0022072.
RX PUBMED: 10831835.
RA Zimmerman C. M., Padgett R. W.
RT Transforming growth factor beta signaling mediators and modulators
RL Gene 249:17-30 (2000).
XX
//


N-terminus [2]. FT 46 170
PS51075; MH1. FT 49 177
MH1 domain [2]. FT 59 168
SM00523; dwAneu5. FT 61 165
PF03165; MH1 domain. FT 73 77
defective Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS) [5]. FT 178 540
Linker region [2]. FT 540 751
PF03166; MH2 domain. FT 541 771
MH2 domain [2]. FT 544 749
SM00524; DWB. FT 546 771
PS51076; MH2.
XX SF in comparison to the Smad-4 homologs and Mad, MEDEA-A (MED) is lacking the SSXS motif at the C-terminus [3]; SF in MEDEA-A (MED)-B exon 4 is missing (73 bps in the linker region) [3]; SF the presence or absence of alternative exon 4 does not affect MEDEA-A (MED) binding activity [3]; SF the first encoded methionine is used as the translational start, although a good Drosophila consensus translational start does not occur until the third methionine, M27 [2]; SF in conflict to SPTREMBL # O61458, here M27 is used as translational start site resulting in an ORF of 745 AAs [1] [4]; SF in conflict to 771 AAs [2]; SF given start and end positions of domains and regions of the protein recruited from reference_no 15907 are in conflict to [1] [3]; SF defective NLS (Nuclear Localization Signal) in comparison to R-Smads [5]; SF after phosphorylation of MAD at the C-terminus it interacts physically with MEDEA-A (MED) [2]; SF MH2 domain of MEDEA-A (MED) is essential for the formation of productive heteromeric MAD/MEDEA-A (MED) complexes, whereas the MH1 domain is not [2]; SF entrance into the nucleus requires physical association with phosphorylated MAD [2]; XX CP embryo: ubiquitously expressed, but at varying levels, during embryonic development [2]; stage 4: widespread transcript localization, maternal contribution [2]; stage7: strong expression in mesoderm and head region [2]; stage 14: throughout ectoderm, endoderm, central nervous system [2]; stage 16: low levels in second midgut constriction, higher levels in central nervous system [2]; [2]. XX FF involved in dpp-signaling, acts downstream of TKV (Thick vein receptor)-receptor (receptor-type I) [1]; FF required for all dpp-dependent signaling in embryonic dorsal-ventral patterning [1] [2]; FF in knock-out studies, null embryos bore fully ventralized cuticles that were indistinguishable from dpp null embryos [2]; FF Embryos with one Medea+ chromosome had a weaker phenotype, indicating that patterning is sensitive to different levels of Medea function [2]; XX BS R10035. BS R10036. BS R10100. XX DR TRANSPATH: MO000019017. DR EMBL: AF019754; AF019754. DR EMBL: AF027729; AF027729. DR UniProtKB: O62609; O62609. DR UniProtKB: Q9U010; Q9U010. DR FLYBASE: FBgn0011655. XX RN [1]; RE0015899. RX PUBMED: 9502722. RA Hudson J. B., Podos S. D., Keith K., Simpson S. L., Ferguson E. L. RT The Drosophila Medea gene is required downstream of dpp and encodes a functional homolog of human Smad4. RL Development 125:1407-1420 (1998). RN [2]; RE0015907. RX PUBMED: 9502724. RA Wisotzkey R. G., Mehra A., Sutherland D. J., Dobens L. L., Liu X., Dohrmann C., Attisano L., Raftery L. A. RT Medea is a Drosophila Smad4 homolog that is differentially required to potentiate DPP responses. RL Development 125:1433-1445 (1998). RN [3]; RE0015913. RX PUBMED: 9694800. RA Xu X., Yin Z., Hudson J. B., Ferguson E. L., Frasch M. RT Smad proteins act in combination with synergistic and antagonistic regulators to target Dpp responses to the Drosophila mesoderm. RL Genes Dev. 12:2354-2370 (1998). RN [4]; RE0015915. RX PUBMED: 9693372. RA Inoue H., Imamura T., Ishidou Y., Takase M., Udagawa Y., Oka Y., Tsuneizumi K., Tabata T., Miyazono K., Kawabata M. RT Interplay of signal mediators of decapentaplegic (Dpp): molecular characterization of mothers against dpp, Medea, and daughters against dpp. RL Mol. Biol. Cell 9:2145-2156 (1998). RN [5]; RE0016203. RX PUBMED: 10884415. RA Xiao Z., Liu X., Henis Y. I., Lodish H. F. RT A distinct nuclear localization signal in the N terminus of Smad 3 determines its ligand-induced nuclear translocation. RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:7853-7858 (2000). RN [6]; RE0022036. RX PUBMED: 10370243. RA Zhang Y., Derynck R. RT Regulation of Smad signalling by protein associations and signalling crosstalk RL Trends Cell Biol. 9:274-279 (1999). RN [7]; RE0022065. RX PUBMED: 10712925. RA Attisano L., Wrana J. L. RT Smads as transcriptional co-modulators RL Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:235-243 (2000). RN [8]; RE0022072. RX PUBMED: 10831835. RA Zimmerman C. M., Padgett R. W. RT Transforming growth factor beta signaling mediators and modulators RL Gene 249:17-30 (2000). XX //