
AC T01315
XX
ID T01315
XX
DT 23.10.1994 (created); ewi.
DT 16.07.2012 (updated); mkl.
CO Copyright (C), QIAGEN.
XX
FA CREMbeta
XX
SY CREMbeta.
XX
OS mouse, Mus musculus
OC eukaryota; animalia; metazoa; chordata; vertebrata; tetrapoda; mammalia; eutheria; rodentia; myomorpha; muridae; murinae
XX
GE G000532 Crem.
XX
CL C0008; bZIP.
XX
SZ 245 AA; 27.4 kDa (cDNA) (calc.).
XX
SQ MSKCGRKKYMRTNVRQMTMETVESQQDRSVTRSVAEHSSAHMQTGQISVPTLAQVATIAE
SQ TDDSADSEVIDSHKRREILSRRPSYRKILNELSSDVPGIPKIEEEKSEEEGTPPNIATMA
SQ VPTSIYQTSTGQYNEETDLAPSHMAAATGDMPTYQIRAPTTALPQGVVMAASPGSLHSPQ
SQ QLAEEATRKRELRLMKNREAAKECRRRKKEYVKCLESRVAVLEVQNKKLIEELETLKDIC
SQ SPKTD
XX
SC Swiss-Prot#P27699-3
XX
FT 36 95  PS50953; KID.
FT 48 88
PS50953; KID.
FT 48 88  PF02173; pKID domain.
FT 84 84
PF02173; pKID domain.
FT 84 84  phosphorylation by PKA [5].
FT 169 226
phosphorylation by PKA [5].
FT 169 226  SM00338; brlzneu.
FT 169 229
SM00338; brlzneu.
FT 169 229  PF00170; bZIP transcription factor.
FT 171 222
PF00170; bZIP transcription factor.
FT 171 222  PS50217; BZIP.
PS50217; BZIP.
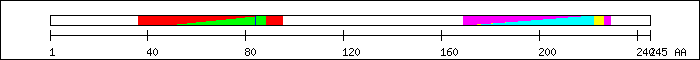 XX
SF encoded by exons 1 (B), 3 (E), 4 (F), 6 (X), 7 (H), and the 3'-half of exon 8 (Ib) [7];
SF several alternative splice variants [1];
SF binds with higher affinity than CREMalpha to a series of different CREs [5];
XX
CP mRNA: pituitary gland, brain, kidney, heart [2].
CN not found in testis [2].
XX
FF repressor, CREB antagonist as dominant negative regulator [1] [5];
FF CREMbeta is upregulated in CREB -/- mice;
FF repressor function is relieved by phosphorylation of Ser-68, presumably by PKA [5];
FF osmotic stimulation of the supraoptic nucleus, induction of CREMbeta (and -alpha) correlates with down-regulation of c-fos [6];
XX
IN T01315 CREMbeta; mouse, Mus musculus.
IN T01319 ICER; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
XX
MX M00981 V$CREBATF_Q6.
MX M00916 V$CREB_Q2_01.
MX M00801 V$CREB_Q3.
MX M00917 V$CREB_Q4_01.
MX M01820 V$CREM_Q6.
MX M08803 V$CREM_Q6_01.
XX
BS R01358.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000003370.
DR EMBL: M60285;
DR UniProtKB: P27699-3;
XX
RN [1]; RE0000262.
RX PUBMED: 1847666.
RA Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription
RL Cell 64:739-749 (1991).
RN [2]; RE0001912.
RX PUBMED: 1370576.
RA Foulkes N. S., Mellstroem B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator
RL Nature 355:80-84 (1992).
RN [3]; RE0001915.
RX PUBMED: 8397338.
RA Stehle J. H., Foulkes N. S., Molina C. A., Simonneaux V., Pevet P., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Adrenergic signals direct rhythmic expression of transcriptional repressor CREM in the pineal gland
RL Nature 365:314-320 (1993).
RN [4]; RE0002563.
RX PUBMED: 8202542.
RA Hummler E., Cole T. J., Blendy J. A., Ganss R., Aguzzi A., Schmid W., Beermann F., Schuetz G.
RT Targeted mutation of the CREB gene: compensation within the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5647-5651 (1994).
RN [5]; RE0003158.
RX PUBMED: 8458330.
RA Laoide B.M., Foulkes N.S., Schlotter F., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT The functional versatility of CREM is determined by its modular structure
RL EMBO J. 12:1179-1191 (1993).
RN [6]; RE0005266.
RX PUBMED: 8386526.
RA Mellstroem B., Naranjo J. R., Foulkes N. S., Lafarga M., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Transcriptional response to cAMP in brain: specific distribution and induction of CREM antagonists
RL Neuron 10:655-665 (1993).
RN [7]; RE0000035.
RX PUBMED: 6537904.
RA Parker C. S., Topol J.
RT A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity
RL Cell 36:357-369 (1984).
XX
//
XX
SF encoded by exons 1 (B), 3 (E), 4 (F), 6 (X), 7 (H), and the 3'-half of exon 8 (Ib) [7];
SF several alternative splice variants [1];
SF binds with higher affinity than CREMalpha to a series of different CREs [5];
XX
CP mRNA: pituitary gland, brain, kidney, heart [2].
CN not found in testis [2].
XX
FF repressor, CREB antagonist as dominant negative regulator [1] [5];
FF CREMbeta is upregulated in CREB -/- mice;
FF repressor function is relieved by phosphorylation of Ser-68, presumably by PKA [5];
FF osmotic stimulation of the supraoptic nucleus, induction of CREMbeta (and -alpha) correlates with down-regulation of c-fos [6];
XX
IN T01315 CREMbeta; mouse, Mus musculus.
IN T01319 ICER; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
XX
MX M00981 V$CREBATF_Q6.
MX M00916 V$CREB_Q2_01.
MX M00801 V$CREB_Q3.
MX M00917 V$CREB_Q4_01.
MX M01820 V$CREM_Q6.
MX M08803 V$CREM_Q6_01.
XX
BS R01358.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000003370.
DR EMBL: M60285;
DR UniProtKB: P27699-3;
XX
RN [1]; RE0000262.
RX PUBMED: 1847666.
RA Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription
RL Cell 64:739-749 (1991).
RN [2]; RE0001912.
RX PUBMED: 1370576.
RA Foulkes N. S., Mellstroem B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator
RL Nature 355:80-84 (1992).
RN [3]; RE0001915.
RX PUBMED: 8397338.
RA Stehle J. H., Foulkes N. S., Molina C. A., Simonneaux V., Pevet P., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Adrenergic signals direct rhythmic expression of transcriptional repressor CREM in the pineal gland
RL Nature 365:314-320 (1993).
RN [4]; RE0002563.
RX PUBMED: 8202542.
RA Hummler E., Cole T. J., Blendy J. A., Ganss R., Aguzzi A., Schmid W., Beermann F., Schuetz G.
RT Targeted mutation of the CREB gene: compensation within the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5647-5651 (1994).
RN [5]; RE0003158.
RX PUBMED: 8458330.
RA Laoide B.M., Foulkes N.S., Schlotter F., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT The functional versatility of CREM is determined by its modular structure
RL EMBO J. 12:1179-1191 (1993).
RN [6]; RE0005266.
RX PUBMED: 8386526.
RA Mellstroem B., Naranjo J. R., Foulkes N. S., Lafarga M., Sassone-Corsi P.
RT Transcriptional response to cAMP in brain: specific distribution and induction of CREM antagonists
RL Neuron 10:655-665 (1993).
RN [7]; RE0000035.
RX PUBMED: 6537904.
RA Parker C. S., Topol J.
RT A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity
RL Cell 36:357-369 (1984).
XX
//


PS50953; KID. FT 48 88
PF02173; pKID domain. FT 84 84
phosphorylation by PKA [5]. FT 169 226
SM00338; brlzneu. FT 169 229
PF00170; bZIP transcription factor. FT 171 222
PS50217; BZIP.
XX SF encoded by exons 1 (B), 3 (E), 4 (F), 6 (X), 7 (H), and the 3'-half of exon 8 (Ib) [7]; SF several alternative splice variants [1]; SF binds with higher affinity than CREMalpha to a series of different CREs [5]; XX CP mRNA: pituitary gland, brain, kidney, heart [2]. CN not found in testis [2]. XX FF repressor, CREB antagonist as dominant negative regulator [1] [5]; FF CREMbeta is upregulated in CREB -/- mice; FF repressor function is relieved by phosphorylation of Ser-68, presumably by PKA [5]; FF osmotic stimulation of the supraoptic nucleus, induction of CREMbeta (and -alpha) correlates with down-regulation of c-fos [6]; XX IN T01315 CREMbeta; mouse, Mus musculus. IN T01319 ICER; rat, Rattus norvegicus. XX MX M00981 V$CREBATF_Q6. MX M00916 V$CREB_Q2_01. MX M00801 V$CREB_Q3. MX M00917 V$CREB_Q4_01. MX M01820 V$CREM_Q6. MX M08803 V$CREM_Q6_01. XX BS R01358. XX DR TRANSPATH: MO000003370. DR EMBL: M60285; DR UniProtKB: P27699-3; XX RN [1]; RE0000262. RX PUBMED: 1847666. RA Foulkes N. S., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P. RT CREM gene: use of alternative DNA-binding domains generates multiple antagonists of cAMP-induced transcription RL Cell 64:739-749 (1991). RN [2]; RE0001912. RX PUBMED: 1370576. RA Foulkes N. S., Mellstroem B., Benusiglio E., Sassone-Corsi P. RT Developmental switch of CREM function during spermatogenesis: from antagonist to activator RL Nature 355:80-84 (1992). RN [3]; RE0001915. RX PUBMED: 8397338. RA Stehle J. H., Foulkes N. S., Molina C. A., Simonneaux V., Pevet P., Sassone-Corsi P. RT Adrenergic signals direct rhythmic expression of transcriptional repressor CREM in the pineal gland RL Nature 365:314-320 (1993). RN [4]; RE0002563. RX PUBMED: 8202542. RA Hummler E., Cole T. J., Blendy J. A., Ganss R., Aguzzi A., Schmid W., Beermann F., Schuetz G. RT Targeted mutation of the CREB gene: compensation within the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5647-5651 (1994). RN [5]; RE0003158. RX PUBMED: 8458330. RA Laoide B.M., Foulkes N.S., Schlotter F., Sassone-Corsi P. RT The functional versatility of CREM is determined by its modular structure RL EMBO J. 12:1179-1191 (1993). RN [6]; RE0005266. RX PUBMED: 8386526. RA Mellstroem B., Naranjo J. R., Foulkes N. S., Lafarga M., Sassone-Corsi P. RT Transcriptional response to cAMP in brain: specific distribution and induction of CREM antagonists RL Neuron 10:655-665 (1993). RN [7]; RE0000035. RX PUBMED: 6537904. RA Parker C. S., Topol J. RT A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity RL Cell 36:357-369 (1984). XX //