
AC T01769
XX
ID T01769
XX
DT 18.04.1996 (created); ewi.
DT 22.07.2015 (updated); sla.
CO Copyright (C), QIAGEN.
XX
FA MEF-2C-isoform2
XX
SY MEF-2C; MEF-2C/delta8; MEF2C; MEF2C isoform 2; MEF2C-isoform2; myocyte enhancer factor 2C.
XX
OS mouse, Mus musculus
OC eukaryota; animalia; metazoa; chordata; vertebrata; tetrapoda; mammalia; eutheria; rodentia; myomorpha; muridae; murinae
XX
GE G005285 Mef2c.
XX
CL C0014; MADS; 5.1.1.1.3.2.
XX
SZ 466 AA; 50.4 kDa (cDNA) (calc.).
XX
SQ MGRKKIQITRIMDERNRQVTFTKRKFGLMKKAYELSVLCDCEIALIIFNSTNKLFQYAST
SQ DMDKVLLKYTEYNEPHESRTNSDIVETLRKKGLNGCDSPDPDADDSVGHSPESEDKYRKI
SQ NEDIDLMISRQRLCAVPPPSFEMPVTIPVSSHNSLVYSNPVSTLGNPNLLPLAHPSLQRN
SQ SMSPGVTHRPPSAGNTGGLMGGDLTSGAGTSAGNGYGNPRNSPGLLVSPGNLNKNIQAKS
SQ PPPMNLGMNNRKPDLRVLIPPGSKNTMPSVNQRINNSQSAQSLATPVVSVATPTLPGQGM
SQ GGYPSAISTTYGTEYSLSSADLSSLSGFNTASALHLGSVTGWQQQHLHNMPPSALSQLGA
SQ CTSTHLSQSSNLSLPSTQSLSIKSEPVSPPRDRTTTPSRYPQHTTRHEAGRSPVDSLSSC
SQ SSSYDGSDREDHRNEFHSPIGLTRPSPDERESPSVKRMRLSEGWAT
XX
SC Swiss-Prot#Q8CFN5-2
XX
FT 1 60  SM00432; MADS.
FT 1 61
SM00432; MADS.
FT 1 61  PS50066; MADS_BOX_2.
FT 9 59
PS50066; MADS_BOX_2.
FT 9 59  PF00319; SRF-type transcription factor (DNA-binding a.
FT 35 48
PF00319; SRF-type transcription factor (DNA-binding a.
FT 35 48  hydrophobic stretch, essential for dimerization [5].
FT 143 174
hydrophobic stretch, essential for dimerization [5].
FT 143 174  trans-activating domain I (TAD I) [5].
FT 175 198
trans-activating domain I (TAD I) [5].
FT 175 198  inhibitory domain [5].
FT 247 327
inhibitory domain [5].
FT 247 327  trans-activating domain II (TAD II) [5].
trans-activating domain II (TAD II) [5].
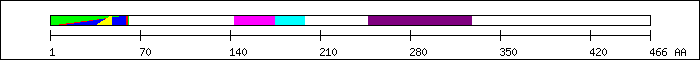 XX
SF alternative splice variants have an insertion of 48 AA after residue 86 or a deletion of 32 AA in the C-terminal region [1];
SF calculated isoelectric point is pI = 8.65 [1];
SF binds to MEF-2 sites [1];
SF gene expression in developing brain see for detailed information [9];
XX
CP very high levels in skeletal muscle, lower in brain, spleen [1]; developing brain [9]; P19 cells differentiated into neurons, C2C12 myotubes (protein level) [10] [9] [10] [1].
CN heart, kidney, liver, stomach, uterus [1]; P19 cells differentiated into endodermal cells, undifferentiated P19 cells, mouse brain (protein level) [10] [10] [1].
XX
FF transcriptional activator [1];
FF cooperates with MyoD through direct interactions and by binding to either MEF-2 sites or to E-box elements [2];
FF myogenin-E12 heterodimers synergistically activate transcription in collaboration with MEF-2C [8];
FF in adult mice and using human sequence information, (human gene) exon A-containing MEF-2C variants (473 and 441 AA forms) have been found in the brain only [4];
FF in embryonic cardiac muscle 7.5 p.c. expression within cardiac mesoderm [6];
FF in embryonic skeletal muscle between 8.5 and 9 p.c.: expression in myocytes within somite myotome [6];
FF expression in cerebellum: in adults highest levels in hippocampus, olfactory bulb [7];
FF synergistic activation of transcription in neurogenic lineages with MASH1 [10];
FF in homozygous null mutation MEF-2C mice, the heart tube did not undergo looping morphogenesis, the future right ventricle did not form, and a subset of cardiac muscle genes was not expressed [3];
FF is an essential regulator of cardiac myogenesis and right ventricular development [3];
FF activated Notch inhibits DNA binding and myogenic activities of MEF-2C [11];
FF p300 augments MEF-2C-dependent transactivation and interacts with the MADS domain of MEF-2C [12];
XX
IN T00526 MyoD; mouse, Mus musculus.
IN T00806 TEF-1; human, Homo sapiens.
XX
MX M02025 V$MEF2C_Q4.
MX M00941 V$MEF2_Q6_01.
MX M07424 V$MEF2_Q6_03.
XX
BS R09226.
BS R09143.
BS R09387.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000025910.
DR EMBL: L13171;
DR UniProtKB: Q8CFN5-2;
XX
RN [1]; RE0004081.
RX PUBMED: 8506376.
RA Martin J. F., Schwarz J. J., Olson E. N.
RT Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF) MEF-2C: A tissue-restricted member of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5282-5286 (1993).
RN [2]; RE0004082.
RX PUBMED: 8548800.
RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N.
RT Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2 and myogenic bHLH proteins
RL Cell 83:1125-1136 (1995).
RN [3]; RE0006359.
RX PUBMED: 9162005.
RA Lin Q., Schwarz J., Bucana C., Olson E. N.
RT Control of mouse cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis by transcription factor MEF2C
RL Science 276:1404-1407 (1997).
RN [4]; RE0006947.
RX PUBMED: 8455629.
RA McDermott J. C., Cardoso M. C., Yu Y.-T., Andres V., Leifer D., Krainc D., Lipton S. A., Nadal-Ginard B.
RT hMEF2C gene encodes skeletal muscle- and brain-specific transcription factors
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:2564-2577 (1993).
RN [5]; RE0006948.
RX PUBMED: 8649370.
RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N.
RT Mutational analysis of the DNA binding, dimerization and transcriptional activation domains of MEF2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2627-2636 (1996).
RN [6]; RE0014840.
RX PUBMED: 8026334.
RA Edmondson D.G., Lyons G.E., Martin J.F., Olson E.N.
RT Mef2 gene expression marks the cardiac and skeletal muscle lineages during mouse embryogenesis
RL Development 120:1251-1263 (1994).
RN [7]; RE0014846.
RX PUBMED: 9013788.
RA Lin X., Shah S., Bulleit R.F.
RT The expression of MEF2 genes is implicated in CNS neuronal differentiation
RL Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 42:307-316 (1996).
RN [8]; RE0015010.
RX PUBMED: 9418854.
RA Black B.L., Molkentin J.D., Olson E.N.
RT Multiple roles for the MyoD basic region in transmission of transcriptional activation signals and interaction with MEF2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:69-77 (1998).
RN [9]; RE0015071.
RX PUBMED: 7643214.
RA Lyons G.E., Micales B.K., Schwarz J., Martin J.F., Olson E.N.
RT Expression of mef2 genes in the mouse central nervous system suggests a role in neuronal maturation
RL J. Neurosci. 15:5727-5738 (1995).
RN [10]; RE0015139.
RX PUBMED: 8900141.
RA Black B.L., Ligon K.L., Zhang Y., Olson E.N.
RT Cooperative transcriptional activation by the neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix protein MASH1 and members of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) family
RL J. Biol. Chem. 271:26659-26663 (1996).
RN [11]; RE0015210.
RX PUBMED: 10082551.
RA Wilson-Rawls J., Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Olson E. N.
RT Activated notch inhibits myogenic activity of the MADS-Box transcription factor myocyte enhancer factor 2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:2853-2862 (1999).
RN [12]; RE0015233.
RX PUBMED: 9001254.
RA Sartorelli V., Huang J., Hamamori Y., Kedes L.
RT Molecular mechanisms of myogenic coactivation by p300: direct interaction with the activation domain of MyoD and with the MADS box of MEF2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:1010-1026 (1997).
RN [13]; RE0041339.
RX PUBMED: 12061776.
RA Maeda T., Gupta M. P., Stewart A. F.
RT TEF-1 and MEF2 transcription factors interact to regulate muscle-specific promoters
RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294:791-7 (2002).
RN [14]; RE0048109.
RX PUBMED: 10817756.
RA Chen S. L., Dowhan D. H., Hosking B. M., Muscat G. E.
RT The steroid receptor coactivator, GRIP-1, is necessary for MEF-2C-dependent gene expression and skeletal muscle differentiation.
RL Genes Dev. 14:1209-1228 (2000).
XX
//
XX
SF alternative splice variants have an insertion of 48 AA after residue 86 or a deletion of 32 AA in the C-terminal region [1];
SF calculated isoelectric point is pI = 8.65 [1];
SF binds to MEF-2 sites [1];
SF gene expression in developing brain see for detailed information [9];
XX
CP very high levels in skeletal muscle, lower in brain, spleen [1]; developing brain [9]; P19 cells differentiated into neurons, C2C12 myotubes (protein level) [10] [9] [10] [1].
CN heart, kidney, liver, stomach, uterus [1]; P19 cells differentiated into endodermal cells, undifferentiated P19 cells, mouse brain (protein level) [10] [10] [1].
XX
FF transcriptional activator [1];
FF cooperates with MyoD through direct interactions and by binding to either MEF-2 sites or to E-box elements [2];
FF myogenin-E12 heterodimers synergistically activate transcription in collaboration with MEF-2C [8];
FF in adult mice and using human sequence information, (human gene) exon A-containing MEF-2C variants (473 and 441 AA forms) have been found in the brain only [4];
FF in embryonic cardiac muscle 7.5 p.c. expression within cardiac mesoderm [6];
FF in embryonic skeletal muscle between 8.5 and 9 p.c.: expression in myocytes within somite myotome [6];
FF expression in cerebellum: in adults highest levels in hippocampus, olfactory bulb [7];
FF synergistic activation of transcription in neurogenic lineages with MASH1 [10];
FF in homozygous null mutation MEF-2C mice, the heart tube did not undergo looping morphogenesis, the future right ventricle did not form, and a subset of cardiac muscle genes was not expressed [3];
FF is an essential regulator of cardiac myogenesis and right ventricular development [3];
FF activated Notch inhibits DNA binding and myogenic activities of MEF-2C [11];
FF p300 augments MEF-2C-dependent transactivation and interacts with the MADS domain of MEF-2C [12];
XX
IN T00526 MyoD; mouse, Mus musculus.
IN T00806 TEF-1; human, Homo sapiens.
XX
MX M02025 V$MEF2C_Q4.
MX M00941 V$MEF2_Q6_01.
MX M07424 V$MEF2_Q6_03.
XX
BS R09226.
BS R09143.
BS R09387.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000025910.
DR EMBL: L13171;
DR UniProtKB: Q8CFN5-2;
XX
RN [1]; RE0004081.
RX PUBMED: 8506376.
RA Martin J. F., Schwarz J. J., Olson E. N.
RT Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF) MEF-2C: A tissue-restricted member of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5282-5286 (1993).
RN [2]; RE0004082.
RX PUBMED: 8548800.
RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N.
RT Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2 and myogenic bHLH proteins
RL Cell 83:1125-1136 (1995).
RN [3]; RE0006359.
RX PUBMED: 9162005.
RA Lin Q., Schwarz J., Bucana C., Olson E. N.
RT Control of mouse cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis by transcription factor MEF2C
RL Science 276:1404-1407 (1997).
RN [4]; RE0006947.
RX PUBMED: 8455629.
RA McDermott J. C., Cardoso M. C., Yu Y.-T., Andres V., Leifer D., Krainc D., Lipton S. A., Nadal-Ginard B.
RT hMEF2C gene encodes skeletal muscle- and brain-specific transcription factors
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:2564-2577 (1993).
RN [5]; RE0006948.
RX PUBMED: 8649370.
RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N.
RT Mutational analysis of the DNA binding, dimerization and transcriptional activation domains of MEF2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2627-2636 (1996).
RN [6]; RE0014840.
RX PUBMED: 8026334.
RA Edmondson D.G., Lyons G.E., Martin J.F., Olson E.N.
RT Mef2 gene expression marks the cardiac and skeletal muscle lineages during mouse embryogenesis
RL Development 120:1251-1263 (1994).
RN [7]; RE0014846.
RX PUBMED: 9013788.
RA Lin X., Shah S., Bulleit R.F.
RT The expression of MEF2 genes is implicated in CNS neuronal differentiation
RL Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 42:307-316 (1996).
RN [8]; RE0015010.
RX PUBMED: 9418854.
RA Black B.L., Molkentin J.D., Olson E.N.
RT Multiple roles for the MyoD basic region in transmission of transcriptional activation signals and interaction with MEF2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:69-77 (1998).
RN [9]; RE0015071.
RX PUBMED: 7643214.
RA Lyons G.E., Micales B.K., Schwarz J., Martin J.F., Olson E.N.
RT Expression of mef2 genes in the mouse central nervous system suggests a role in neuronal maturation
RL J. Neurosci. 15:5727-5738 (1995).
RN [10]; RE0015139.
RX PUBMED: 8900141.
RA Black B.L., Ligon K.L., Zhang Y., Olson E.N.
RT Cooperative transcriptional activation by the neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix protein MASH1 and members of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) family
RL J. Biol. Chem. 271:26659-26663 (1996).
RN [11]; RE0015210.
RX PUBMED: 10082551.
RA Wilson-Rawls J., Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Olson E. N.
RT Activated notch inhibits myogenic activity of the MADS-Box transcription factor myocyte enhancer factor 2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:2853-2862 (1999).
RN [12]; RE0015233.
RX PUBMED: 9001254.
RA Sartorelli V., Huang J., Hamamori Y., Kedes L.
RT Molecular mechanisms of myogenic coactivation by p300: direct interaction with the activation domain of MyoD and with the MADS box of MEF2C
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:1010-1026 (1997).
RN [13]; RE0041339.
RX PUBMED: 12061776.
RA Maeda T., Gupta M. P., Stewart A. F.
RT TEF-1 and MEF2 transcription factors interact to regulate muscle-specific promoters
RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294:791-7 (2002).
RN [14]; RE0048109.
RX PUBMED: 10817756.
RA Chen S. L., Dowhan D. H., Hosking B. M., Muscat G. E.
RT The steroid receptor coactivator, GRIP-1, is necessary for MEF-2C-dependent gene expression and skeletal muscle differentiation.
RL Genes Dev. 14:1209-1228 (2000).
XX
//


SM00432; MADS. FT 1 61
PS50066; MADS_BOX_2. FT 9 59
PF00319; SRF-type transcription factor (DNA-binding a. FT 35 48
hydrophobic stretch, essential for dimerization [5]. FT 143 174
trans-activating domain I (TAD I) [5]. FT 175 198
inhibitory domain [5]. FT 247 327
trans-activating domain II (TAD II) [5].
XX SF alternative splice variants have an insertion of 48 AA after residue 86 or a deletion of 32 AA in the C-terminal region [1]; SF calculated isoelectric point is pI = 8.65 [1]; SF binds to MEF-2 sites [1]; SF gene expression in developing brain see for detailed information [9]; XX CP very high levels in skeletal muscle, lower in brain, spleen [1]; developing brain [9]; P19 cells differentiated into neurons, C2C12 myotubes (protein level) [10] [9] [10] [1]. CN heart, kidney, liver, stomach, uterus [1]; P19 cells differentiated into endodermal cells, undifferentiated P19 cells, mouse brain (protein level) [10] [10] [1]. XX FF transcriptional activator [1]; FF cooperates with MyoD through direct interactions and by binding to either MEF-2 sites or to E-box elements [2]; FF myogenin-E12 heterodimers synergistically activate transcription in collaboration with MEF-2C [8]; FF in adult mice and using human sequence information, (human gene) exon A-containing MEF-2C variants (473 and 441 AA forms) have been found in the brain only [4]; FF in embryonic cardiac muscle 7.5 p.c. expression within cardiac mesoderm [6]; FF in embryonic skeletal muscle between 8.5 and 9 p.c.: expression in myocytes within somite myotome [6]; FF expression in cerebellum: in adults highest levels in hippocampus, olfactory bulb [7]; FF synergistic activation of transcription in neurogenic lineages with MASH1 [10]; FF in homozygous null mutation MEF-2C mice, the heart tube did not undergo looping morphogenesis, the future right ventricle did not form, and a subset of cardiac muscle genes was not expressed [3]; FF is an essential regulator of cardiac myogenesis and right ventricular development [3]; FF activated Notch inhibits DNA binding and myogenic activities of MEF-2C [11]; FF p300 augments MEF-2C-dependent transactivation and interacts with the MADS domain of MEF-2C [12]; XX IN T00526 MyoD; mouse, Mus musculus. IN T00806 TEF-1; human, Homo sapiens. XX MX M02025 V$MEF2C_Q4. MX M00941 V$MEF2_Q6_01. MX M07424 V$MEF2_Q6_03. XX BS R09226. BS R09143. BS R09387. XX DR TRANSPATH: MO000025910. DR EMBL: L13171; DR UniProtKB: Q8CFN5-2; XX RN [1]; RE0004081. RX PUBMED: 8506376. RA Martin J. F., Schwarz J. J., Olson E. N. RT Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF) MEF-2C: A tissue-restricted member of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5282-5286 (1993). RN [2]; RE0004082. RX PUBMED: 8548800. RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N. RT Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2 and myogenic bHLH proteins RL Cell 83:1125-1136 (1995). RN [3]; RE0006359. RX PUBMED: 9162005. RA Lin Q., Schwarz J., Bucana C., Olson E. N. RT Control of mouse cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis by transcription factor MEF2C RL Science 276:1404-1407 (1997). RN [4]; RE0006947. RX PUBMED: 8455629. RA McDermott J. C., Cardoso M. C., Yu Y.-T., Andres V., Leifer D., Krainc D., Lipton S. A., Nadal-Ginard B. RT hMEF2C gene encodes skeletal muscle- and brain-specific transcription factors RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:2564-2577 (1993). RN [5]; RE0006948. RX PUBMED: 8649370. RA Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N. RT Mutational analysis of the DNA binding, dimerization and transcriptional activation domains of MEF2C RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2627-2636 (1996). RN [6]; RE0014840. RX PUBMED: 8026334. RA Edmondson D.G., Lyons G.E., Martin J.F., Olson E.N. RT Mef2 gene expression marks the cardiac and skeletal muscle lineages during mouse embryogenesis RL Development 120:1251-1263 (1994). RN [7]; RE0014846. RX PUBMED: 9013788. RA Lin X., Shah S., Bulleit R.F. RT The expression of MEF2 genes is implicated in CNS neuronal differentiation RL Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 42:307-316 (1996). RN [8]; RE0015010. RX PUBMED: 9418854. RA Black B.L., Molkentin J.D., Olson E.N. RT Multiple roles for the MyoD basic region in transmission of transcriptional activation signals and interaction with MEF2 RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:69-77 (1998). RN [9]; RE0015071. RX PUBMED: 7643214. RA Lyons G.E., Micales B.K., Schwarz J., Martin J.F., Olson E.N. RT Expression of mef2 genes in the mouse central nervous system suggests a role in neuronal maturation RL J. Neurosci. 15:5727-5738 (1995). RN [10]; RE0015139. RX PUBMED: 8900141. RA Black B.L., Ligon K.L., Zhang Y., Olson E.N. RT Cooperative transcriptional activation by the neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix protein MASH1 and members of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) family RL J. Biol. Chem. 271:26659-26663 (1996). RN [11]; RE0015210. RX PUBMED: 10082551. RA Wilson-Rawls J., Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Olson E. N. RT Activated notch inhibits myogenic activity of the MADS-Box transcription factor myocyte enhancer factor 2C RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:2853-2862 (1999). RN [12]; RE0015233. RX PUBMED: 9001254. RA Sartorelli V., Huang J., Hamamori Y., Kedes L. RT Molecular mechanisms of myogenic coactivation by p300: direct interaction with the activation domain of MyoD and with the MADS box of MEF2C RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:1010-1026 (1997). RN [13]; RE0041339. RX PUBMED: 12061776. RA Maeda T., Gupta M. P., Stewart A. F. RT TEF-1 and MEF2 transcription factors interact to regulate muscle-specific promoters RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 294:791-7 (2002). RN [14]; RE0048109. RX PUBMED: 10817756. RA Chen S. L., Dowhan D. H., Hosking B. M., Muscat G. E. RT The steroid receptor coactivator, GRIP-1, is necessary for MEF-2C-dependent gene expression and skeletal muscle differentiation. RL Genes Dev. 14:1209-1228 (2000). XX //