
AC T00647
XX
ID T00647
XX
DT 15.10.1992 (created); ewi.
DT 31.05.2016 (updated); sup.
CO Copyright (C), QIAGEN.
XX
FA Oct-2
XX
SY IgNF-A; NF-A; NF-A2; NF-III; Oct-2; Oct-2A; Octamer binding factor 2; OTF-2; OTF-2A.
XX
OS human, Homo sapiens
OC eukaryota; animalia; metazoa; chordata; vertebrata; tetrapoda; mammalia; eutheria; primates
XX
GE G003935 POU2F2; HGNC: POU2F2.
XX
CL C0007; POU; 3.1.10.2.2.
XX
SZ 479 AA; 51.2 kDa (cDNA) (calc.), 58.5, 61, 62 kDa (SDS) [3] [3]
XX
SQ MVHSSMGAPEIRMSKPLEAEKQGLDSPSEHTDTERNGPDTNHQNPQNKTSPFSVSPTGPS
SQ TKIKAEDPSGDSAPAAPLPPQPAQPHLPQAQLMLTGSQLAGDIQQLLQLQQLVLVPGHHL
SQ QPPAQFLLPQAQQSQPGLLPTPNLFQLPQQTQGALLTSQPRAGLPTQAVTRPTLPDPHLS
SQ HPQPPKCLEPPSHPEEPSDLEELEQFARTFKQRRIKLGFTQGDVGLAMGKLYGNDFSQTT
SQ ISRFEALNLSFKNMCKLKPLLEKWLNDAETMSVDSSLPSPNQLSSPSLGFDGLPGRRRKK
SQ RTSIETNVRFALEKSFLANQKPTSEEILLIAEQLHMEKEVIRVWFCNRRQKEKRINPCSA
SQ APMLPSPGKPASYSPHMVTPQGGAGTLPLSQASSSLSTTVTTLSSAVGTLHPSRTAGGGG
SQ GGGGAAPPLNSIPSVTPPPPATTNSTNPSPQGSHSAIGLSGLNPSTGPGLWWNPAPYQP
XX
SC Swiss-Prot#P09086, supplemented by an additional N-terminal Met according to [19] [13]
XX
FT 2 99  repressing domain [41].
FT 102 116
repressing domain [41].
FT 102 116  trans-activating domain I (Q domain) [6].
FT 168 183
trans-activating domain I (Q domain) [6].
FT 168 183  missing in Oct-2 of [19].
FT 195 269
missing in Oct-2 of [19].
FT 195 269  PF00157; Pou domain - N-terminal to homeobox domain.
FT 195 269
PF00157; Pou domain - N-terminal to homeobox domain.
FT 195 269  SM00352; pou.
FT 295 355
SM00352; pou.
FT 295 355  PS50071; HOMEOBOX_2.
FT 295 357
PS50071; HOMEOBOX_2.
FT 295 357  PS50550; POU_HOMEODOMAIN.
FT 297 359
PS50550; POU_HOMEODOMAIN.
FT 297 359  SM00389; HOX_1.
FT 298 354
SM00389; HOX_1.
FT 298 354  PF00046; Homeobox domain.
FT 462 479
PF00046; Homeobox domain.
FT 462 479  trans-activating domain II (P domain) [6].
trans-activating domain II (P domain) [6].
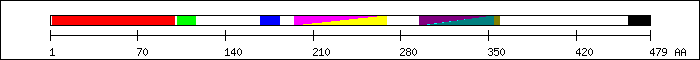 XX
SF two Oct-2 sequences differing in the 16 AA stretch at 168-183 may represent splice variants, a third one is Oct-2B [19] [21];
SF bipartite DNA-binding domain with POUs and POUh domain [45] [1];
SF three Oct-2A-related peptides in B cells [3];
SF interacting with octamer (high-affinity) and with heptamer (low-affinity) elements [14] [5] [15];
SF the low-affinity elements with 1000-fold lower affinity [14];
SF within the IgH enhancer, both elements adjacent to each other cooperatively bind two Oct-2 molecules [14];
SF even higher affinity of one Oct-2 molecule for the composite motif ATGCTAATGARAT [32];
SF however, Oct-2 does not interact with viral VP16 unless Ala-317 is replaced by Glu as in Oct-1 [36] [37];
SF DNA-binding specificity indistinguishable from that of Oct-1 [3];
SF POUs induces bending of the bound octamer DNA [11];
SF whole POU domain interacts with the C-terminal core domain of TBP [38];
SF 2 synergizing trans-activating domains [39] [41] [6] [8];
SF the first two modularly acting Gln-clusters within the N-terminal activation domain are particularly important [46] [8];
SF for full effect, C-terminal extensions of this domain are required [6] [8];
SF it possibly depends on additional factors [39] [41];
SF and it is reported to activate exclusively from proximal binding sites, whereas activation from distantly located binding sites requires the C-terminal activation domain II [35];
SF activation domain II depends on an additional B-cell specific activity [41] [43];
SF B-cell specific activity as Bob1/OBF-I [40] [47] [48];
SF Bob1/OBF-1 interacts with the POU domain [40];
XX
CP lymphoid cells.
XX
FF activator [12];
FF actively supporting assembly of basal transcription complex [44];
FF has to be present for many rounds of transcription [44];
FF expressed in CD4+, but not in CD8+ T cells;
FF enhanced by ionomycin, ionomycin + PMA, or antigen [30];
FF down-regulated by IFN-alpha or TPA [33];
FF extinguished in B cell x fibroblast cell hybrids, leading to extinction of Ig gene expression as well [9] [4];
XX
IN T02187 MAT1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T02141 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T09163 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00643 POU2F1; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T00794 TBP; human, Homo sapiens.
XX
MX M01368 V$OCT2_01.
MX M03836 V$OCT2_Q6.
MX M00210 V$OCT_C.
MX M00795 V$OCT_Q6.
MX M04072 V$POU2F2_02.
MX M04715 V$POU2F2_06.
MX M07120 V$POU2F2_08.
MX M08836 V$POU2F2_09.
XX
BS R01176.
BS R30580.
BS R73424.
BS R73429.
BS R73430.
BS R73431.
BS R73432.
BS R73433.
BS R73434.
BS R73435.
BS R73436.
BS R73437.
BS R73438.
BS R73439.
BS R73440.
BS R73441.
BS R73442.
BS R73443.
BS R55823.
BS R31087.
BS R31091.
BS R31090.
BS R65648.
BS R40723.
BS R42511.
BS R21557.
BS R00557.
BS R00663.
BS R59453.
BS R01636.
BS R01637.
BS R14543.
BS R04234.
BS R01089.
BS R42509.
BS R08500.
BS R68580.
BS R35619.
BS R35707.
BS R28117.
BS R39915.
BS R32242.
BS R39912.
BS R13391.
BS R72729.
BS R00841.
BS R00842.
BS R00861.
BS R00870.
BS R00892.
BS R00894.
BS R02953.
BS R13571.
BS R02226.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000035134.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00158.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00365.
DR EMBL: M36542;
DR EMBL: M36653;
DR EMBL: X13809;
DR EMBL: X81030;
DR UniProtKB: P09086;
DR PDB: 1hdp.
XX
RN [1]; RE0000064.
RX PUBMED: 2901913.
RA Ko H.-S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M.
RT A Human Protein Specific for the Immunoglobulin Octamer DNA Motif Contains a Functional Homeobox Domain
RL Cell 55:135-144 (1988).
RN [2]; RE0000088.
RX PUBMED: 3091258.
RA Sen R., Baltimore D.
RT Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences
RL Cell 46:705-716 (1986).
RN [3]; RE0000094.
RX PUBMED: 3119226.
RA Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification and Purification of a Human Lymphoid-Specific Octamer-Binding Protein (OTF-2) That Activates Transcription of an Immunoglobulin Promoter In Vitro
RL Cell 51:783-793 (1987).
RN [4]; RE0000095.
RX PUBMED: 2110507.
RA Junker S., Pedersen S., Schreiber E., Matthias P.
RT Extinction of an immunoglobulin promoter in cell hybrids is mediated by the octamer motif and correlates with suppression of Oct-2 expression
RL Cell 61:467-474 (1990).
RN [5]; RE0000352.
RX PUBMED: 2507313.
RA Kemler I., Schreiber E., Mueller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W.
RT Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the heavy chain promoter
RL EMBO J. 8:2001-2008 (1989).
RN [6]; RE0000353.
RX PUBMED: 2328729.
RA Gerster T., Balmaceda C.-G., Roeder R. G.
RT The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription
RL EMBO J. 9:1635-1643 (1990).
RN [7]; RE0000369.
RX PUBMED: 3072196.
RA Schreiber E., Matthias P., Mueller M. M., Schaffner W.
RT Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA)
RL EMBO J. 7:4221-4229 (1988).
RN [8]; RE0000370.
RX PUBMED: 2328728.
RA Mueller-Immerglueck M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P.
RT Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells
RL EMBO J. 9:1625-1634 (1990).
RN [9]; RE0000371.
RX PUBMED: 2107075.
RA Bergmann Y., Strich B., Sharir H., Ber R., Laskov R.
RT Extinction of Ig genes expression in myeloma x fibroblast somatic cell hybrids is accompanied by repression of the oct-2 gene encoding a B-cell specific transcription factor
RL EMBO J. 9:849-855 (1990).
RN [10]; RE0000424.
RX PUBMED: 2573524.
RA Schoeler H. R., Balling R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Suzuki N., Gruss P.
RT Octamer binding proteins confer transcriptional activity in early mouse embryogenesis
RL EMBO J. 8:2551-2557 (1989).
RN [11]; RE0000528.
RX PUBMED: 1915275.
RA Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A. W. M., van Weperen W. W., van der Vliet P. C.
RT POU proteins bend DNA via the POU-specific domain
RL EMBO J. 10:3007-3014 (1991).
RN [12]; RE0000606.
RX PUBMED: 3264542.
RA LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A.
RT Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro
RL Genes Dev. 2:1227-1237 (1988).
RN [13]; RE0000621.
RX PUBMED: 3265124.
RA Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A.
RT The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains
RL Genes Dev. 2:1570-1581 (1988).
RN [14]; RE0000626.
RX PUBMED: 2612908.
RA LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A.
RT The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites
RL Genes Dev. 3:1625-1638 (1989).
RN [15]; RE0001291.
RX PUBMED: 2710122.
RA Poellinger L., Roeder R. G.
RT Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:747-756 (1989).
RN [16]; RE0001367.
RX PUBMED: 2113179.
RA Nelms K., van Ness B.
RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Human Kappa Light-Chain Enhancer
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:3843-3846 (1990).
RN [17]; RE0001404.
RX PUBMED: 2511430.
RA Currie R. A., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Mouse Kappa Light-Chain Immunoglobulin Enhancer
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:4239-4247 (1989).
RN [18]; RE0001488.
RX PUBMED: 2204815.
RA Kamps M. P., Corcoran L., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D.
RT The promoter of the human interleukin-2 gene contains two octamer-binding sites and is partially activated by the expression of Oct-2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:5464-5472 (1990).
RN [19]; RE0001778.
RX PUBMED: 2904654.
RA Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C.-G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G.
RT A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homeobox protein
RL Nature 336:551-557 (1988).
RN [20]; RE0001800.
RX PUBMED: 3095662.
RA Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D.
RT A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes
RL Nature 323:640-643 (1986).
RN [21]; RE0001806.
RX PUBMED: 2904653.
RA Mueller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P.
RT A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells
RL Nature 336:544-551 (1988).
RN [22]; RE0002003.
RX PUBMED: 3131743.
RA Mocikat R., Pruijn G. J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Zachau H. G.
RT An ACCC-containing protein-binding sequence in the neighbourhood of the decanucleotide recognition site of the immunoglobulin gene promoter
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 16:3693 (1988).
RN [23]; RE0002050.
RX PUBMED: 2472607.
RA Lloyd J. A., Lee R. F., Lingrel L. B.
RT Mutations in two regions upstream of the Agamma globin gene canonical promoter affect gene expression
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:4339-4352 (1989).
RN [24]; RE0002056.
RX PUBMED: 2555786.
RA Shibuya H., Taniguchi T.
RT Identification of multiple cis-elements and trans-acting factors involved in the induced expression of human IL-2 gene
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:9173-9184 (1989).
RN [25]; RE0002297.
RX PUBMED: 3462701.
RA Sive H. L., Roeder R. G.
RT Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:6382-6386 (1986).
RN [26]; RE0002310.
RX PUBMED: 2842768.
RA Gerster T., Roeder R. G.
RT A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:6347-6351 (1988).
RN [27]; RE0002378.
RX PUBMED: 2508087.
RA Hermanson G. G., Briskin M., Sigman D., Wall R.
RT Immunoglobulin enhancer and promoter motifs 5' of the B29 B-cell-specific gene
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:7341-7345 (1989).
RN [28]; RE0002612.
RX PUBMED: 3399892.
RA Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D.
RT Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif
RL Science 241:577-580 (1988).
RN [29]; RE0002767.
RX PUBMED: 2109187.
RA Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification of a novel factor that interacts with an immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter and stimulates transcription in conjunction with the lymphoid cell-specific factor OTF2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:2145-2153 (1990).
RN [30]; RE0003066.
RX PUBMED: 1620122.
RA Kang S.-M., Tsang W., Doll S., Scherle P., Ko H.-S., Tran A.-C., Lenardo M. J., Staudt L. M.
RT Induction of the POU domain transcription factor Oct-2 during T-cell activation by cognate antigen
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3149-3154 (1992).
RN [31]; RE0004194.
RX PUBMED: 2302733.
RA Tanaka M., Herr W.
RT Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation
RL Cell 60:375-386 (1990).
RN [32]; RE0004197.
RX PUBMED: 1650186.
RA Dent C. L., Latchman D. S.
RT The overlapping octamer/TAATGARAT motif is a high-affinity binding site for the cellular transcription factors Oct-1 and Oct-2
RL Biochem. J. 277:541-545 (1991).
RN [33]; RE0004199.
RX PUBMED: 1939139.
RA Dent C. L., Lillycrop K. A., Bybee A., Latchman D. S., Thomas N. S. B.
RT Interferon-a treatment of Daudi cells down-regulates the octamer binding transcription/DNA replication factors Oct-1 and Oct-2
RL J. Biol. Chem. 266:20888-20892 (1991).
RN [34]; RE0004204.
RX PUBMED: 1739980.
RA Tanaka M., Lai J.-S., Herr W.
RT Promoter-selective activation domains in Oct-1 and Oct-2 direct differential activation of an snRNA and mRNA promoter
RL Cell 68:755-767 (1992).
RN [35]; RE0004207.
RX PUBMED: 1464321.
RA Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W.
RT Different activation domains stimulte transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions
RL EMBO J. 11:4961-4968 (1992).
RN [36]; RE0004209.
RX PUBMED: 1358756.
RA Lai J.-S., Cleary M. A., Herr W.
RT A single amino acid exchange transfers VP16-induced positive control from the Oct-1 to the Oct-2 homeo domain
RL Genes Dev. 6:2058-2065 (1992).
RN [37]; RE0004210.
RX PUBMED: 1358755.
RA Pomerantz J. L., Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A.
RT Recognition of the surface of a homeo domain protein
RL Genes Dev. 6:2047-2057 (1992).
RN [38]; RE0004220.
RX PUBMED: 8202368.
RA Zwilling S., Annweiler A., Wirth T.
RT The POU domains of the Oct1 and Oct2 transcription factors mediate specific interaction with TBP
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 22:1655-1662 (1994).
RN [39]; RE0004282.
RX PUBMED: 8065338.
RA Tanaka M., Clouston W. M., Herr W.
RT The Oct-2 glutamine-rich and proline-rich activation domains can synergize with each other or duplicates of themselves to activate transcription
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6046-6055 (1994).
RN [40]; RE0004283.
RX PUBMED: 7779176.
RA Gstaiger M., Knoepfel L., Georgiev O., Schaffner W., Hovens C. M.
RT A B-cell coactivator of octamer-binding transcription factors
RL Nature 373:360-362 (1995).
RN [41]; RE0004284.
RX PUBMED: 8529657.
RA Friedl E. M., Matthias P.
RT Transcriptional activation and repression, two properties of the lymphoid-specific transcription factor Oct-2a
RL Eur. J. Biochem. 234:308-316 (1995).
RN [42]; RE0004286.
RX PUBMED: 2123291.
RA Pierani A., Heguy A., Fujii H., Roeder R. G.
RT Activation of octamer-containing promoters by either octamer-binding transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) or OTF-2 and requirement of an additional B-cell-specific component for optimal transcription of immunoglobulin promoters
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:6204-6215 (1990).
RN [43]; RE0004287.
RX PUBMED: 1620119.
RA Annweiler A., Mueller-Immerglueck M., Wirth T.
RT Oct2 transactivation from a remote enhancer position requires a B-cell-restricted activity
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3107-3116 (1992).
RN [44]; RE0004289.
RX PUBMED: 8428575.
RA Arnosti D. N., Merino A., Reinberg D., Schaffner W.
RT Oct-2 facilitates functional preinitiation complex assembly and is continuously required at the promoter for multiple rounds of transcription
RL EMBO J. 12:157-166 (1993).
RN [45]; RE0004291.
RX PUBMED: 8171007.
RA Jancso A., Botfield M. C., Sowers L. C., Weiss M. A.
RT An altered-specificity mutation in a human POU domain demonstrates functional analogy between the POU-specific subdomain and phage l repressor
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:3887-3891 (1994).
RN [46]; RE0004293.
RX PUBMED: 8065339.
RA Tanaka M., Herr W.
RT Reconstitution of transcriptional activation domains by reiteration of short peptide segments reveals the modular organization of a glutamine-rich activation domain
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6056-6067 (1994).
RN [47]; RE0004399.
RX PUBMED: 1423591.
RA Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G.
RT A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglogulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription
RL Cell 71:231-241 (1992).
RN [48]; RE0004442.
RX PUBMED: 7859290.
RA Strubin M., Newell J. W., Matthias P.
RT OBF-1, a novel B cell-specific coactivator that stimulates immunoglobulin promoter activity through association with octamer-binding proteins
RL Cell 80:497-506 (1995).
RN [49]; RE0066536.
RX PUBMED: 16186795.
RA Heckman C. A., Duan H., Garcia P. B., Boxer L. M.
RT Oct transcription factors mediate t(14;18) lymphoma cell survival by directly regulating bcl-2 expression.
RL Oncogene 25:888-898 (2006).
XX
//
XX
SF two Oct-2 sequences differing in the 16 AA stretch at 168-183 may represent splice variants, a third one is Oct-2B [19] [21];
SF bipartite DNA-binding domain with POUs and POUh domain [45] [1];
SF three Oct-2A-related peptides in B cells [3];
SF interacting with octamer (high-affinity) and with heptamer (low-affinity) elements [14] [5] [15];
SF the low-affinity elements with 1000-fold lower affinity [14];
SF within the IgH enhancer, both elements adjacent to each other cooperatively bind two Oct-2 molecules [14];
SF even higher affinity of one Oct-2 molecule for the composite motif ATGCTAATGARAT [32];
SF however, Oct-2 does not interact with viral VP16 unless Ala-317 is replaced by Glu as in Oct-1 [36] [37];
SF DNA-binding specificity indistinguishable from that of Oct-1 [3];
SF POUs induces bending of the bound octamer DNA [11];
SF whole POU domain interacts with the C-terminal core domain of TBP [38];
SF 2 synergizing trans-activating domains [39] [41] [6] [8];
SF the first two modularly acting Gln-clusters within the N-terminal activation domain are particularly important [46] [8];
SF for full effect, C-terminal extensions of this domain are required [6] [8];
SF it possibly depends on additional factors [39] [41];
SF and it is reported to activate exclusively from proximal binding sites, whereas activation from distantly located binding sites requires the C-terminal activation domain II [35];
SF activation domain II depends on an additional B-cell specific activity [41] [43];
SF B-cell specific activity as Bob1/OBF-I [40] [47] [48];
SF Bob1/OBF-1 interacts with the POU domain [40];
XX
CP lymphoid cells.
XX
FF activator [12];
FF actively supporting assembly of basal transcription complex [44];
FF has to be present for many rounds of transcription [44];
FF expressed in CD4+, but not in CD8+ T cells;
FF enhanced by ionomycin, ionomycin + PMA, or antigen [30];
FF down-regulated by IFN-alpha or TPA [33];
FF extinguished in B cell x fibroblast cell hybrids, leading to extinction of Ig gene expression as well [9] [4];
XX
IN T02187 MAT1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T02141 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T09163 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00643 POU2F1; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T00794 TBP; human, Homo sapiens.
XX
MX M01368 V$OCT2_01.
MX M03836 V$OCT2_Q6.
MX M00210 V$OCT_C.
MX M00795 V$OCT_Q6.
MX M04072 V$POU2F2_02.
MX M04715 V$POU2F2_06.
MX M07120 V$POU2F2_08.
MX M08836 V$POU2F2_09.
XX
BS R01176.
BS R30580.
BS R73424.
BS R73429.
BS R73430.
BS R73431.
BS R73432.
BS R73433.
BS R73434.
BS R73435.
BS R73436.
BS R73437.
BS R73438.
BS R73439.
BS R73440.
BS R73441.
BS R73442.
BS R73443.
BS R55823.
BS R31087.
BS R31091.
BS R31090.
BS R65648.
BS R40723.
BS R42511.
BS R21557.
BS R00557.
BS R00663.
BS R59453.
BS R01636.
BS R01637.
BS R14543.
BS R04234.
BS R01089.
BS R42509.
BS R08500.
BS R68580.
BS R35619.
BS R35707.
BS R28117.
BS R39915.
BS R32242.
BS R39912.
BS R13391.
BS R72729.
BS R00841.
BS R00842.
BS R00861.
BS R00870.
BS R00892.
BS R00894.
BS R02953.
BS R13571.
BS R02226.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000035134.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00158.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00365.
DR EMBL: M36542;
DR EMBL: M36653;
DR EMBL: X13809;
DR EMBL: X81030;
DR UniProtKB: P09086;
DR PDB: 1hdp.
XX
RN [1]; RE0000064.
RX PUBMED: 2901913.
RA Ko H.-S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M.
RT A Human Protein Specific for the Immunoglobulin Octamer DNA Motif Contains a Functional Homeobox Domain
RL Cell 55:135-144 (1988).
RN [2]; RE0000088.
RX PUBMED: 3091258.
RA Sen R., Baltimore D.
RT Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences
RL Cell 46:705-716 (1986).
RN [3]; RE0000094.
RX PUBMED: 3119226.
RA Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification and Purification of a Human Lymphoid-Specific Octamer-Binding Protein (OTF-2) That Activates Transcription of an Immunoglobulin Promoter In Vitro
RL Cell 51:783-793 (1987).
RN [4]; RE0000095.
RX PUBMED: 2110507.
RA Junker S., Pedersen S., Schreiber E., Matthias P.
RT Extinction of an immunoglobulin promoter in cell hybrids is mediated by the octamer motif and correlates with suppression of Oct-2 expression
RL Cell 61:467-474 (1990).
RN [5]; RE0000352.
RX PUBMED: 2507313.
RA Kemler I., Schreiber E., Mueller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W.
RT Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the heavy chain promoter
RL EMBO J. 8:2001-2008 (1989).
RN [6]; RE0000353.
RX PUBMED: 2328729.
RA Gerster T., Balmaceda C.-G., Roeder R. G.
RT The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription
RL EMBO J. 9:1635-1643 (1990).
RN [7]; RE0000369.
RX PUBMED: 3072196.
RA Schreiber E., Matthias P., Mueller M. M., Schaffner W.
RT Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA)
RL EMBO J. 7:4221-4229 (1988).
RN [8]; RE0000370.
RX PUBMED: 2328728.
RA Mueller-Immerglueck M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P.
RT Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells
RL EMBO J. 9:1625-1634 (1990).
RN [9]; RE0000371.
RX PUBMED: 2107075.
RA Bergmann Y., Strich B., Sharir H., Ber R., Laskov R.
RT Extinction of Ig genes expression in myeloma x fibroblast somatic cell hybrids is accompanied by repression of the oct-2 gene encoding a B-cell specific transcription factor
RL EMBO J. 9:849-855 (1990).
RN [10]; RE0000424.
RX PUBMED: 2573524.
RA Schoeler H. R., Balling R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Suzuki N., Gruss P.
RT Octamer binding proteins confer transcriptional activity in early mouse embryogenesis
RL EMBO J. 8:2551-2557 (1989).
RN [11]; RE0000528.
RX PUBMED: 1915275.
RA Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A. W. M., van Weperen W. W., van der Vliet P. C.
RT POU proteins bend DNA via the POU-specific domain
RL EMBO J. 10:3007-3014 (1991).
RN [12]; RE0000606.
RX PUBMED: 3264542.
RA LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A.
RT Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro
RL Genes Dev. 2:1227-1237 (1988).
RN [13]; RE0000621.
RX PUBMED: 3265124.
RA Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A.
RT The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains
RL Genes Dev. 2:1570-1581 (1988).
RN [14]; RE0000626.
RX PUBMED: 2612908.
RA LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A.
RT The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites
RL Genes Dev. 3:1625-1638 (1989).
RN [15]; RE0001291.
RX PUBMED: 2710122.
RA Poellinger L., Roeder R. G.
RT Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:747-756 (1989).
RN [16]; RE0001367.
RX PUBMED: 2113179.
RA Nelms K., van Ness B.
RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Human Kappa Light-Chain Enhancer
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:3843-3846 (1990).
RN [17]; RE0001404.
RX PUBMED: 2511430.
RA Currie R. A., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Mouse Kappa Light-Chain Immunoglobulin Enhancer
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:4239-4247 (1989).
RN [18]; RE0001488.
RX PUBMED: 2204815.
RA Kamps M. P., Corcoran L., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D.
RT The promoter of the human interleukin-2 gene contains two octamer-binding sites and is partially activated by the expression of Oct-2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:5464-5472 (1990).
RN [19]; RE0001778.
RX PUBMED: 2904654.
RA Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C.-G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G.
RT A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homeobox protein
RL Nature 336:551-557 (1988).
RN [20]; RE0001800.
RX PUBMED: 3095662.
RA Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D.
RT A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes
RL Nature 323:640-643 (1986).
RN [21]; RE0001806.
RX PUBMED: 2904653.
RA Mueller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P.
RT A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells
RL Nature 336:544-551 (1988).
RN [22]; RE0002003.
RX PUBMED: 3131743.
RA Mocikat R., Pruijn G. J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Zachau H. G.
RT An ACCC-containing protein-binding sequence in the neighbourhood of the decanucleotide recognition site of the immunoglobulin gene promoter
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 16:3693 (1988).
RN [23]; RE0002050.
RX PUBMED: 2472607.
RA Lloyd J. A., Lee R. F., Lingrel L. B.
RT Mutations in two regions upstream of the Agamma globin gene canonical promoter affect gene expression
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:4339-4352 (1989).
RN [24]; RE0002056.
RX PUBMED: 2555786.
RA Shibuya H., Taniguchi T.
RT Identification of multiple cis-elements and trans-acting factors involved in the induced expression of human IL-2 gene
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:9173-9184 (1989).
RN [25]; RE0002297.
RX PUBMED: 3462701.
RA Sive H. L., Roeder R. G.
RT Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:6382-6386 (1986).
RN [26]; RE0002310.
RX PUBMED: 2842768.
RA Gerster T., Roeder R. G.
RT A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:6347-6351 (1988).
RN [27]; RE0002378.
RX PUBMED: 2508087.
RA Hermanson G. G., Briskin M., Sigman D., Wall R.
RT Immunoglobulin enhancer and promoter motifs 5' of the B29 B-cell-specific gene
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:7341-7345 (1989).
RN [28]; RE0002612.
RX PUBMED: 3399892.
RA Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D.
RT Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif
RL Science 241:577-580 (1988).
RN [29]; RE0002767.
RX PUBMED: 2109187.
RA Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G.
RT Identification of a novel factor that interacts with an immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter and stimulates transcription in conjunction with the lymphoid cell-specific factor OTF2
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:2145-2153 (1990).
RN [30]; RE0003066.
RX PUBMED: 1620122.
RA Kang S.-M., Tsang W., Doll S., Scherle P., Ko H.-S., Tran A.-C., Lenardo M. J., Staudt L. M.
RT Induction of the POU domain transcription factor Oct-2 during T-cell activation by cognate antigen
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3149-3154 (1992).
RN [31]; RE0004194.
RX PUBMED: 2302733.
RA Tanaka M., Herr W.
RT Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation
RL Cell 60:375-386 (1990).
RN [32]; RE0004197.
RX PUBMED: 1650186.
RA Dent C. L., Latchman D. S.
RT The overlapping octamer/TAATGARAT motif is a high-affinity binding site for the cellular transcription factors Oct-1 and Oct-2
RL Biochem. J. 277:541-545 (1991).
RN [33]; RE0004199.
RX PUBMED: 1939139.
RA Dent C. L., Lillycrop K. A., Bybee A., Latchman D. S., Thomas N. S. B.
RT Interferon-a treatment of Daudi cells down-regulates the octamer binding transcription/DNA replication factors Oct-1 and Oct-2
RL J. Biol. Chem. 266:20888-20892 (1991).
RN [34]; RE0004204.
RX PUBMED: 1739980.
RA Tanaka M., Lai J.-S., Herr W.
RT Promoter-selective activation domains in Oct-1 and Oct-2 direct differential activation of an snRNA and mRNA promoter
RL Cell 68:755-767 (1992).
RN [35]; RE0004207.
RX PUBMED: 1464321.
RA Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W.
RT Different activation domains stimulte transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions
RL EMBO J. 11:4961-4968 (1992).
RN [36]; RE0004209.
RX PUBMED: 1358756.
RA Lai J.-S., Cleary M. A., Herr W.
RT A single amino acid exchange transfers VP16-induced positive control from the Oct-1 to the Oct-2 homeo domain
RL Genes Dev. 6:2058-2065 (1992).
RN [37]; RE0004210.
RX PUBMED: 1358755.
RA Pomerantz J. L., Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A.
RT Recognition of the surface of a homeo domain protein
RL Genes Dev. 6:2047-2057 (1992).
RN [38]; RE0004220.
RX PUBMED: 8202368.
RA Zwilling S., Annweiler A., Wirth T.
RT The POU domains of the Oct1 and Oct2 transcription factors mediate specific interaction with TBP
RL Nucleic Acids Res. 22:1655-1662 (1994).
RN [39]; RE0004282.
RX PUBMED: 8065338.
RA Tanaka M., Clouston W. M., Herr W.
RT The Oct-2 glutamine-rich and proline-rich activation domains can synergize with each other or duplicates of themselves to activate transcription
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6046-6055 (1994).
RN [40]; RE0004283.
RX PUBMED: 7779176.
RA Gstaiger M., Knoepfel L., Georgiev O., Schaffner W., Hovens C. M.
RT A B-cell coactivator of octamer-binding transcription factors
RL Nature 373:360-362 (1995).
RN [41]; RE0004284.
RX PUBMED: 8529657.
RA Friedl E. M., Matthias P.
RT Transcriptional activation and repression, two properties of the lymphoid-specific transcription factor Oct-2a
RL Eur. J. Biochem. 234:308-316 (1995).
RN [42]; RE0004286.
RX PUBMED: 2123291.
RA Pierani A., Heguy A., Fujii H., Roeder R. G.
RT Activation of octamer-containing promoters by either octamer-binding transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) or OTF-2 and requirement of an additional B-cell-specific component for optimal transcription of immunoglobulin promoters
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:6204-6215 (1990).
RN [43]; RE0004287.
RX PUBMED: 1620119.
RA Annweiler A., Mueller-Immerglueck M., Wirth T.
RT Oct2 transactivation from a remote enhancer position requires a B-cell-restricted activity
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3107-3116 (1992).
RN [44]; RE0004289.
RX PUBMED: 8428575.
RA Arnosti D. N., Merino A., Reinberg D., Schaffner W.
RT Oct-2 facilitates functional preinitiation complex assembly and is continuously required at the promoter for multiple rounds of transcription
RL EMBO J. 12:157-166 (1993).
RN [45]; RE0004291.
RX PUBMED: 8171007.
RA Jancso A., Botfield M. C., Sowers L. C., Weiss M. A.
RT An altered-specificity mutation in a human POU domain demonstrates functional analogy between the POU-specific subdomain and phage l repressor
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:3887-3891 (1994).
RN [46]; RE0004293.
RX PUBMED: 8065339.
RA Tanaka M., Herr W.
RT Reconstitution of transcriptional activation domains by reiteration of short peptide segments reveals the modular organization of a glutamine-rich activation domain
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6056-6067 (1994).
RN [47]; RE0004399.
RX PUBMED: 1423591.
RA Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G.
RT A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglogulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription
RL Cell 71:231-241 (1992).
RN [48]; RE0004442.
RX PUBMED: 7859290.
RA Strubin M., Newell J. W., Matthias P.
RT OBF-1, a novel B cell-specific coactivator that stimulates immunoglobulin promoter activity through association with octamer-binding proteins
RL Cell 80:497-506 (1995).
RN [49]; RE0066536.
RX PUBMED: 16186795.
RA Heckman C. A., Duan H., Garcia P. B., Boxer L. M.
RT Oct transcription factors mediate t(14;18) lymphoma cell survival by directly regulating bcl-2 expression.
RL Oncogene 25:888-898 (2006).
XX
//


repressing domain [41]. FT 102 116
trans-activating domain I (Q domain) [6]. FT 168 183
missing in Oct-2 of [19]. FT 195 269
PF00157; Pou domain - N-terminal to homeobox domain. FT 195 269
SM00352; pou. FT 295 355
PS50071; HOMEOBOX_2. FT 295 357
PS50550; POU_HOMEODOMAIN. FT 297 359
SM00389; HOX_1. FT 298 354
PF00046; Homeobox domain. FT 462 479
trans-activating domain II (P domain) [6].
XX SF two Oct-2 sequences differing in the 16 AA stretch at 168-183 may represent splice variants, a third one is Oct-2B [19] [21]; SF bipartite DNA-binding domain with POUs and POUh domain [45] [1]; SF three Oct-2A-related peptides in B cells [3]; SF interacting with octamer (high-affinity) and with heptamer (low-affinity) elements [14] [5] [15]; SF the low-affinity elements with 1000-fold lower affinity [14]; SF within the IgH enhancer, both elements adjacent to each other cooperatively bind two Oct-2 molecules [14]; SF even higher affinity of one Oct-2 molecule for the composite motif ATGCTAATGARAT [32]; SF however, Oct-2 does not interact with viral VP16 unless Ala-317 is replaced by Glu as in Oct-1 [36] [37]; SF DNA-binding specificity indistinguishable from that of Oct-1 [3]; SF POUs induces bending of the bound octamer DNA [11]; SF whole POU domain interacts with the C-terminal core domain of TBP [38]; SF 2 synergizing trans-activating domains [39] [41] [6] [8]; SF the first two modularly acting Gln-clusters within the N-terminal activation domain are particularly important [46] [8]; SF for full effect, C-terminal extensions of this domain are required [6] [8]; SF it possibly depends on additional factors [39] [41]; SF and it is reported to activate exclusively from proximal binding sites, whereas activation from distantly located binding sites requires the C-terminal activation domain II [35]; SF activation domain II depends on an additional B-cell specific activity [41] [43]; SF B-cell specific activity as Bob1/OBF-I [40] [47] [48]; SF Bob1/OBF-1 interacts with the POU domain [40]; XX CP lymphoid cells. XX FF activator [12]; FF actively supporting assembly of basal transcription complex [44]; FF has to be present for many rounds of transcription [44]; FF expressed in CD4+, but not in CD8+ T cells; FF enhanced by ionomycin, ionomycin + PMA, or antigen [30]; FF down-regulated by IFN-alpha or TPA [33]; FF extinguished in B cell x fibroblast cell hybrids, leading to extinction of Ig gene expression as well [9] [4]; XX IN T02187 MAT1; human, Homo sapiens. IN T02141 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens. IN T09163 OCA-B; human, Homo sapiens. IN T00643 POU2F1; rat, Rattus norvegicus. IN T00794 TBP; human, Homo sapiens. XX MX M01368 V$OCT2_01. MX M03836 V$OCT2_Q6. MX M00210 V$OCT_C. MX M00795 V$OCT_Q6. MX M04072 V$POU2F2_02. MX M04715 V$POU2F2_06. MX M07120 V$POU2F2_08. MX M08836 V$POU2F2_09. XX BS R01176. BS R30580. BS R73424. BS R73429. BS R73430. BS R73431. BS R73432. BS R73433. BS R73434. BS R73435. BS R73436. BS R73437. BS R73438. BS R73439. BS R73440. BS R73441. BS R73442. BS R73443. BS R55823. BS R31087. BS R31091. BS R31090. BS R65648. BS R40723. BS R42511. BS R21557. BS R00557. BS R00663. BS R59453. BS R01636. BS R01637. BS R14543. BS R04234. BS R01089. BS R42509. BS R08500. BS R68580. BS R35619. BS R35707. BS R28117. BS R39915. BS R32242. BS R39912. BS R13391. BS R72729. BS R00841. BS R00842. BS R00861. BS R00870. BS R00892. BS R00894. BS R02953. BS R13571. BS R02226. XX DR TRANSPATH: MO000035134. DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00158. DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00365. DR EMBL: M36542; DR EMBL: M36653; DR EMBL: X13809; DR EMBL: X81030; DR UniProtKB: P09086; DR PDB: 1hdp. XX RN [1]; RE0000064. RX PUBMED: 2901913. RA Ko H.-S., Fast P., McBride W., Staudt L. M. RT A Human Protein Specific for the Immunoglobulin Octamer DNA Motif Contains a Functional Homeobox Domain RL Cell 55:135-144 (1988). RN [2]; RE0000088. RX PUBMED: 3091258. RA Sen R., Baltimore D. RT Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences RL Cell 46:705-716 (1986). RN [3]; RE0000094. RX PUBMED: 3119226. RA Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. RT Identification and Purification of a Human Lymphoid-Specific Octamer-Binding Protein (OTF-2) That Activates Transcription of an Immunoglobulin Promoter In Vitro RL Cell 51:783-793 (1987). RN [4]; RE0000095. RX PUBMED: 2110507. RA Junker S., Pedersen S., Schreiber E., Matthias P. RT Extinction of an immunoglobulin promoter in cell hybrids is mediated by the octamer motif and correlates with suppression of Oct-2 expression RL Cell 61:467-474 (1990). RN [5]; RE0000352. RX PUBMED: 2507313. RA Kemler I., Schreiber E., Mueller M. M., Matthias P., Schaffner W. RT Octamer transcription factors bind to two different sequence motifs of the heavy chain promoter RL EMBO J. 8:2001-2008 (1989). RN [6]; RE0000353. RX PUBMED: 2328729. RA Gerster T., Balmaceda C.-G., Roeder R. G. RT The cell type-specific octamer transcription factor OTF-2 has two domains required for the activation of transcription RL EMBO J. 9:1635-1643 (1990). RN [7]; RE0000369. RX PUBMED: 3072196. RA Schreiber E., Matthias P., Mueller M. M., Schaffner W. RT Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA) RL EMBO J. 7:4221-4229 (1988). RN [8]; RE0000370. RX PUBMED: 2328728. RA Mueller-Immerglueck M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. RT Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells RL EMBO J. 9:1625-1634 (1990). RN [9]; RE0000371. RX PUBMED: 2107075. RA Bergmann Y., Strich B., Sharir H., Ber R., Laskov R. RT Extinction of Ig genes expression in myeloma x fibroblast somatic cell hybrids is accompanied by repression of the oct-2 gene encoding a B-cell specific transcription factor RL EMBO J. 9:849-855 (1990). RN [10]; RE0000424. RX PUBMED: 2573524. RA Schoeler H. R., Balling R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Suzuki N., Gruss P. RT Octamer binding proteins confer transcriptional activity in early mouse embryogenesis RL EMBO J. 8:2551-2557 (1989). RN [11]; RE0000528. RX PUBMED: 1915275. RA Verrijzer C. P., van Oosterhout J. A. W. M., van Weperen W. W., van der Vliet P. C. RT POU proteins bend DNA via the POU-specific domain RL EMBO J. 10:3007-3014 (1991). RN [12]; RE0000606. RX PUBMED: 3264542. RA LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. RT Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro RL Genes Dev. 2:1227-1237 (1988). RN [13]; RE0000621. RX PUBMED: 3265124. RA Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. RT The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains RL Genes Dev. 2:1570-1581 (1988). RN [14]; RE0000626. RX PUBMED: 2612908. RA LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A. RT The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites RL Genes Dev. 3:1625-1638 (1989). RN [15]; RE0001291. RX PUBMED: 2710122. RA Poellinger L., Roeder R. G. RT Octamer transcription factors 1 and 2 each bind to two different functional elements in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:747-756 (1989). RN [16]; RE0001367. RX PUBMED: 2113179. RA Nelms K., van Ness B. RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Human Kappa Light-Chain Enhancer RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:3843-3846 (1990). RN [17]; RE0001404. RX PUBMED: 2511430. RA Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. RT Identification of an Octamer-Binding Site in the Mouse Kappa Light-Chain Immunoglobulin Enhancer RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:4239-4247 (1989). RN [18]; RE0001488. RX PUBMED: 2204815. RA Kamps M. P., Corcoran L., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D. RT The promoter of the human interleukin-2 gene contains two octamer-binding sites and is partially activated by the expression of Oct-2 RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:5464-5472 (1990). RN [19]; RE0001778. RX PUBMED: 2904654. RA Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C.-G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. RT A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homeobox protein RL Nature 336:551-557 (1988). RN [20]; RE0001800. RX PUBMED: 3095662. RA Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. RT A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes RL Nature 323:640-643 (1986). RN [21]; RE0001806. RX PUBMED: 2904653. RA Mueller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. RT A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells RL Nature 336:544-551 (1988). RN [22]; RE0002003. RX PUBMED: 3131743. RA Mocikat R., Pruijn G. J. M., van der Vliet P. C., Zachau H. G. RT An ACCC-containing protein-binding sequence in the neighbourhood of the decanucleotide recognition site of the immunoglobulin gene promoter RL Nucleic Acids Res. 16:3693 (1988). RN [23]; RE0002050. RX PUBMED: 2472607. RA Lloyd J. A., Lee R. F., Lingrel L. B. RT Mutations in two regions upstream of the Agamma globin gene canonical promoter affect gene expression RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:4339-4352 (1989). RN [24]; RE0002056. RX PUBMED: 2555786. RA Shibuya H., Taniguchi T. RT Identification of multiple cis-elements and trans-acting factors involved in the induced expression of human IL-2 gene RL Nucleic Acids Res. 17:9173-9184 (1989). RN [25]; RE0002297. RX PUBMED: 3462701. RA Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. RT Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:6382-6386 (1986). RN [26]; RE0002310. RX PUBMED: 2842768. RA Gerster T., Roeder R. G. RT A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:6347-6351 (1988). RN [27]; RE0002378. RX PUBMED: 2508087. RA Hermanson G. G., Briskin M., Sigman D., Wall R. RT Immunoglobulin enhancer and promoter motifs 5' of the B29 B-cell-specific gene RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:7341-7345 (1989). RN [28]; RE0002612. RX PUBMED: 3399892. RA Staudt L. M., Clerc R. G., Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. RT Cloning of a lymphoid-specific cDNA encoding a protein binding the regulatory octamer DNA motif RL Science 241:577-580 (1988). RN [29]; RE0002767. RX PUBMED: 2109187. RA Yoza B. K., Roeder R. G. RT Identification of a novel factor that interacts with an immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter and stimulates transcription in conjunction with the lymphoid cell-specific factor OTF2 RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:2145-2153 (1990). RN [30]; RE0003066. RX PUBMED: 1620122. RA Kang S.-M., Tsang W., Doll S., Scherle P., Ko H.-S., Tran A.-C., Lenardo M. J., Staudt L. M. RT Induction of the POU domain transcription factor Oct-2 during T-cell activation by cognate antigen RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3149-3154 (1992). RN [31]; RE0004194. RX PUBMED: 2302733. RA Tanaka M., Herr W. RT Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation RL Cell 60:375-386 (1990). RN [32]; RE0004197. RX PUBMED: 1650186. RA Dent C. L., Latchman D. S. RT The overlapping octamer/TAATGARAT motif is a high-affinity binding site for the cellular transcription factors Oct-1 and Oct-2 RL Biochem. J. 277:541-545 (1991). RN [33]; RE0004199. RX PUBMED: 1939139. RA Dent C. L., Lillycrop K. A., Bybee A., Latchman D. S., Thomas N. S. B. RT Interferon-a treatment of Daudi cells down-regulates the octamer binding transcription/DNA replication factors Oct-1 and Oct-2 RL J. Biol. Chem. 266:20888-20892 (1991). RN [34]; RE0004204. RX PUBMED: 1739980. RA Tanaka M., Lai J.-S., Herr W. RT Promoter-selective activation domains in Oct-1 and Oct-2 direct differential activation of an snRNA and mRNA promoter RL Cell 68:755-767 (1992). RN [35]; RE0004207. RX PUBMED: 1464321. RA Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. RT Different activation domains stimulte transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions RL EMBO J. 11:4961-4968 (1992). RN [36]; RE0004209. RX PUBMED: 1358756. RA Lai J.-S., Cleary M. A., Herr W. RT A single amino acid exchange transfers VP16-induced positive control from the Oct-1 to the Oct-2 homeo domain RL Genes Dev. 6:2058-2065 (1992). RN [37]; RE0004210. RX PUBMED: 1358755. RA Pomerantz J. L., Kristie T. M., Sharp P. A. RT Recognition of the surface of a homeo domain protein RL Genes Dev. 6:2047-2057 (1992). RN [38]; RE0004220. RX PUBMED: 8202368. RA Zwilling S., Annweiler A., Wirth T. RT The POU domains of the Oct1 and Oct2 transcription factors mediate specific interaction with TBP RL Nucleic Acids Res. 22:1655-1662 (1994). RN [39]; RE0004282. RX PUBMED: 8065338. RA Tanaka M., Clouston W. M., Herr W. RT The Oct-2 glutamine-rich and proline-rich activation domains can synergize with each other or duplicates of themselves to activate transcription RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6046-6055 (1994). RN [40]; RE0004283. RX PUBMED: 7779176. RA Gstaiger M., Knoepfel L., Georgiev O., Schaffner W., Hovens C. M. RT A B-cell coactivator of octamer-binding transcription factors RL Nature 373:360-362 (1995). RN [41]; RE0004284. RX PUBMED: 8529657. RA Friedl E. M., Matthias P. RT Transcriptional activation and repression, two properties of the lymphoid-specific transcription factor Oct-2a RL Eur. J. Biochem. 234:308-316 (1995). RN [42]; RE0004286. RX PUBMED: 2123291. RA Pierani A., Heguy A., Fujii H., Roeder R. G. RT Activation of octamer-containing promoters by either octamer-binding transcription factor 1 (OTF-1) or OTF-2 and requirement of an additional B-cell-specific component for optimal transcription of immunoglobulin promoters RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:6204-6215 (1990). RN [43]; RE0004287. RX PUBMED: 1620119. RA Annweiler A., Mueller-Immerglueck M., Wirth T. RT Oct2 transactivation from a remote enhancer position requires a B-cell-restricted activity RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:3107-3116 (1992). RN [44]; RE0004289. RX PUBMED: 8428575. RA Arnosti D. N., Merino A., Reinberg D., Schaffner W. RT Oct-2 facilitates functional preinitiation complex assembly and is continuously required at the promoter for multiple rounds of transcription RL EMBO J. 12:157-166 (1993). RN [45]; RE0004291. RX PUBMED: 8171007. RA Jancso A., Botfield M. C., Sowers L. C., Weiss M. A. RT An altered-specificity mutation in a human POU domain demonstrates functional analogy between the POU-specific subdomain and phage l repressor RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:3887-3891 (1994). RN [46]; RE0004293. RX PUBMED: 8065339. RA Tanaka M., Herr W. RT Reconstitution of transcriptional activation domains by reiteration of short peptide segments reveals the modular organization of a glutamine-rich activation domain RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:6056-6067 (1994). RN [47]; RE0004399. RX PUBMED: 1423591. RA Luo Y., Fujii H., Gerster T., Roeder R. G. RT A novel B cell-derived coactivator potentiates the activation of immunoglogulin promoters by octamer-binding transcription RL Cell 71:231-241 (1992). RN [48]; RE0004442. RX PUBMED: 7859290. RA Strubin M., Newell J. W., Matthias P. RT OBF-1, a novel B cell-specific coactivator that stimulates immunoglobulin promoter activity through association with octamer-binding proteins RL Cell 80:497-506 (1995). RN [49]; RE0066536. RX PUBMED: 16186795. RA Heckman C. A., Duan H., Garcia P. B., Boxer L. M. RT Oct transcription factors mediate t(14;18) lymphoma cell survival by directly regulating bcl-2 expression. RL Oncogene 25:888-898 (2006). XX //