
AC T00696
XX
ID T00696
XX
DT 15.10.1992 (created); ewi.
DT 30.01.2015 (updated); sup.
CO Copyright (C), QIAGEN.
XX
FA PR B
XX
SY NR3C3; NR3C3b; PR; PR B; progesterone receptor; progesterone receptor form B; progesterone receptor isoform B.
XX
OS human, Homo sapiens
OC eukaryota; animalia; metazoa; chordata; vertebrata; tetrapoda; mammalia; eutheria; primates
XX
GE G003936 PGR; HGNC: PGR.
XX
CL C0002; CC (rec); 2.1.1.1.3.2.
XX
SZ 933 AA; 99.0 kDa (cDNA) (calc.), 114-120 kDa (SDS)
XX
SQ MTELKAKGPRAPHVAGGPPSPEVGSPLLCRPAAGPFPGSQTSDTLPEVSAIPISLDGLLF
SQ PRPCQGQDPSDEKTQDQQSLSDVEGAYSRAEATRGAGGSSSSPPEKDSGLLDSVLDTLLA
SQ PSGPGQSQPSPPACEVTSSWCLFGPELPEDPPAAPATQRVLSPLMSRSGCKVGDSSGTAA
SQ AHKVLPRGLSPARQLLLPASESPHWSGAPVKPSPQAAAVEVEEEDSSESEESAGPLLKGK
SQ PRALGGAAAGGGAAACPPGAAAGGVALVPKEDSRFSAPRVALVEQDAPMAPGRSPLATTV
SQ MDFIHVPILPLNHALLAARTRQLLEDESYDGGAGAASAFAPPRTSPCASSTPVAVGDFPD
SQ CAYPPDAEPKDDAYPLYSDFQPPALKIKEEEEGAEASARSPRSYLVAGANPAAFPDFPLG
SQ PPPPLPPRATPSRPGEAAVTAAPASASVSSASSSGSTLECILYKAEGAPPQQGPFAPPPC
SQ KAPGASGCLLPRDGLPSTSASAAAAGAAPALYPALGLNGLPQLGYQAAVLKEGLPQVYPP
SQ YLNYLRPDSEASQSPQYSFESLPQKICLICGDEASGCHYGVLTCGSCKVFFKRAMEGQHN
SQ YLCAGRNDCIVDKIRRKNCPACRLRKCCQAGMVLGGRKFKKFNKVRVVRALDAVALPQPL
SQ GVPNESQALSQRFTFSPGQDIQLIPPLINLLMSIEPDVIYAGHDNTKPDTSSSLLTSLNQ
SQ LGERQLLSVVKWSKSLPGFRNLHIDDQITLIQYSWMSLMVFGLGWRSYKHVSGQMLYFAP
SQ DLILNEQRMKESSFYSLCLTMWQIPQEFVKLQVSQEEFLCMKVLLLLNTIPLEGLRSQTQ
SQ FEEMRSSYIRELIKAIGLRQKGVVSSSQRFYQLTKLLDNLHDLVKQLHLYCLNTFIQSRA
SQ LSVEFPEMMSEVIAAQLPKILAGMVKPLLFHKK
XX
SC translated from EMBL:M15716
XX
FT 1 564  PF02161; Progesterone receptor.
FT 264 745
PF02161; Progesterone receptor.
FT 264 745  PF00478; IMP dehydrogenase / GMP reductase domai.
FT 564 635
PF00478; IMP dehydrogenase / GMP reductase domai.
FT 564 635  SM00399; c4gold.
FT 564 639
SM00399; c4gold.
FT 564 639  PS51030; NUCLEAR_REC_DBD_2.
FT 565 640
PS51030; NUCLEAR_REC_DBD_2.
FT 565 640  PF00105; Zinc finger, C4 type (two domains).
FT 720 884
PF00105; Zinc finger, C4 type (two domains).
FT 720 884  SM00430; holi.
FT 723 908
SM00430; holi.
FT 723 908  PF00104; Ligand-binding domain of nuclear hormon.
FT 904 918
PF00104; Ligand-binding domain of nuclear hormon.
FT 904 918  AF-2 domain (transactivation activity) [12].
AF-2 domain (transactivation activity) [12].
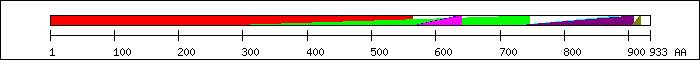 XX
SF alternative promoter usage and, concomitantly, alternative translation initiation gives rise to isoform A T01661 [2];
SF dimerization and nuclear translocation is inhibited by hsp90 [4];
XX
FF activator or repressor in response to progesterone;
FF both PR isoforms exhibit different promoter specificity [2];
XX
IN T08740 batf3; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T18805 batf3; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T04074 brca1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T06595 C/EBPbeta-FL; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T06596 C/EBPbeta-LIP; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T01487 cyclinA; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T02776 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T09944 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00992 Hsp90; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08741 jdp2; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T19032 jdp2; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T01661 PR A; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00696 PR B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08891 PSF-isoform1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08171 PSF; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T21552 SRC-1; Mammalia.
IN T02121 TAFII110; fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster.
XX
MX M00960 V$PR_Q2.
MX M03799 V$PR_Q6.
XX
BS R00973.
BS R00974.
BS R00975.
BS R00976.
BS R00978.
BS R40171.
BS R40172.
BS R40173.
BS R66028.
BS R71596.
BS R71599.
BS R14315.
BS R14316.
BS R12328.
BS R12329.
BS R39279.
BS R34883.
BS R23811.
BS R71581.
BS R71583.
BS R57486.
BS R57499.
BS R57502.
BS R57508.
BS R02234.
BS R29385.
BS R57260.
BS R34881.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000019617.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00603.
DR PATHODB: MT010691.
DR EMBL: M15716; HSPGRR.
DR EMBL: X51730; HSPREC.
DR UniProtKB: P06401-1;
XX
RN [1]; RE0000379.
RX PUBMED: 3416833.
RA Hecht A., Berkenstam A., Stroemstedt P.-E., Gustafsson J.-A., Sippel A. E.
RT A progesterone responsive element maps to the far upstream steroid DNase hypersensitive site of chicken lysozyme chromatin
RL EMBO J. 7:2063-2073 (1988).
RN [2]; RE0000463.
RX PUBMED: 2328727.
RA Kastner P., Krust A., Turcotte B., Stropp U., Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P.
RT Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B
RL EMBO J. 9:1603-1614 (1990).
RN [3]; RE0001752.
RX PUBMED: 2172797.
RA Forman B. M., Samuels H. H.
RT Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 4:1293-1301 (1990).
RN [4]; RE0002418.
RX PUBMED: 1986383.
RA DeMarzo A. M., Beck C. A., Onate S. A., Edwards D. P.
RT Dimerization of mammalian progesterone receptors occurs in the absence of DNA and is related to the release of the 90-kDa heat shock protein
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:72-76 (1991).
RN [5]; RE0003737.
RX PUBMED: 3283939.
RA Evans R. M.
RT The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily
RL Science 240:889-895 (1988).
RN [6]; RE0003738.
RX PUBMED: 1587864.
RA Meyer M.-E., Quirin-Stricker C., Lerouge T., Bocqel M.-T., Gronemeyer H.
RT A limiting factor mediates the differential activation of promoters by the human progesterone receptor isoforms
RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:10882-10887 (1992).
RN [7]; RE0003739.
RX PUBMED: 1518826.
RA Rehberger P., Rexin M., Gehring U.
RT Heterotetrameric structure of the human progesterone receptor
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8001-8005 (1992).
RN [8]; RE0003740.
RX PUBMED: 1312348.
RA Edwards D. P., Estes P. A., Fadok V. A., Bona B. J., Onate S., Nordeen S. K., Welch W. J.
RT Heat shock alters the composition of the heteromeric steroid receptor complexes and enhances receptor activity in vivo
RL Biochemistry 31:2482-2491 (1992).
RN [9]; RE0003745.
RX PUBMED: 3551956.
RA Misrahi M., Atger M., D'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guichon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E.
RT Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem
RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 143:740-748 (1987).
RN [10]; RE0003750.
RX PUBMED: 1730721.
RA Shemshedini L., Ji J., Brou C., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H.
RT In vivo acticity of the transcription activation functions of the progesterone receptor
RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:1834-1839 (1992).
RN [11]; RE0013625.
RX PUBMED: 10219237.
RA Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee.
RT A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily
RL Cell 97:161-163 (1999).
RN [12]; RE0016449.
RX PUBMED: 10428842.
RA Hong H., Yang L., Stallcup M. R.
RT Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3
RL J. Biol. Chem. 274:22618-22626 (1999).
RN [13]; RE0030408.
RX PUBMED: 12771131.
RA Agoulnik I. U., Krause W. C., Bingman W. E. 3rd, Rahman H. T., Amrikachi M., Ayala G. E., Weigel N. L.
RT Repressors of androgen and progesterone receptor action.
RL J. Biol. Chem. 278:31136-48 (2003).
RN [14]; RE0044354.
RX PUBMED: 11773445.
RA Christian M., Pohnke Y., Kempf R., Gellersen B., Brosens J. J.
RT Functional association of PR and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta isoforms: promoter-dependent cooperation between PR-B and liver-enriched inhibitory protein, or liver-enriched activatory protein and PR-A in human endometrial stromal cells
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 16:141-54 (2002).
RN [15]; RE0047476.
RX PUBMED: 12101239.
RA Wardell S. E., Boonyaratanakornkit V., Adelman J. S., Aronheim A., Edwards D. P.
RT Jun dimerization protein 2 functions as a progesterone receptor N-terminal domain coactivator.
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:5451-5466 (2002).
RN [16]; RE0047660.
RX PUBMED: 12727880.
RA Wiper-Bergeron N., Wu D., Pope L., Schild-Poulter C., Hache R. J.
RT Stimulation of preadipocyte differentiation by steroid through targeting of an HDAC1 complex.
RL EMBO J. 22:2135-2145 (2003).
RN [17]; RE0047842.
RX PUBMED: 15668243.
RA Dong X., Shylnova O., Challis J. R., Lye S. J.
RT Identification and characterization of the protein-associated splicing factor as a negative co-regulator of the progesterone receptor.
RL J. Biol. Chem. 280:13329-13340 (2005).
RN [18]; RE0051005.
RX PUBMED: 16109739.
RA Ma Y., Katiyar P., Jones L. P., Fan S., Zhang Y., Furth P. A., Rosen E. M.
RT The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 regulates progesterone receptor signaling in mammary epithelial cells.
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 20:14-34 (2006).
RN [19]; RE0054750.
RX PUBMED: 15486045.
RA Skildum A., Faivre E., Lange C. A.
RT Progesterone receptors induce cell cycle progression via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases.
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 19:327-339 (2005).
XX
//
XX
SF alternative promoter usage and, concomitantly, alternative translation initiation gives rise to isoform A T01661 [2];
SF dimerization and nuclear translocation is inhibited by hsp90 [4];
XX
FF activator or repressor in response to progesterone;
FF both PR isoforms exhibit different promoter specificity [2];
XX
IN T08740 batf3; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T18805 batf3; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T04074 brca1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T06595 C/EBPbeta-FL; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T06596 C/EBPbeta-LIP; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T01487 cyclinA; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T02776 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T09944 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00992 Hsp90; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08741 jdp2; rat, Rattus norvegicus.
IN T19032 jdp2; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T01661 PR A; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T00696 PR B; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08891 PSF-isoform1; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T08171 PSF; human, Homo sapiens.
IN T21552 SRC-1; Mammalia.
IN T02121 TAFII110; fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster.
XX
MX M00960 V$PR_Q2.
MX M03799 V$PR_Q6.
XX
BS R00973.
BS R00974.
BS R00975.
BS R00976.
BS R00978.
BS R40171.
BS R40172.
BS R40173.
BS R66028.
BS R71596.
BS R71599.
BS R14315.
BS R14316.
BS R12328.
BS R12329.
BS R39279.
BS R34883.
BS R23811.
BS R71581.
BS R71583.
BS R57486.
BS R57499.
BS R57502.
BS R57508.
BS R02234.
BS R29385.
BS R57260.
BS R34881.
XX
DR TRANSPATH: MO000019617.
DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00603.
DR PATHODB: MT010691.
DR EMBL: M15716; HSPGRR.
DR EMBL: X51730; HSPREC.
DR UniProtKB: P06401-1;
XX
RN [1]; RE0000379.
RX PUBMED: 3416833.
RA Hecht A., Berkenstam A., Stroemstedt P.-E., Gustafsson J.-A., Sippel A. E.
RT A progesterone responsive element maps to the far upstream steroid DNase hypersensitive site of chicken lysozyme chromatin
RL EMBO J. 7:2063-2073 (1988).
RN [2]; RE0000463.
RX PUBMED: 2328727.
RA Kastner P., Krust A., Turcotte B., Stropp U., Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P.
RT Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B
RL EMBO J. 9:1603-1614 (1990).
RN [3]; RE0001752.
RX PUBMED: 2172797.
RA Forman B. M., Samuels H. H.
RT Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 4:1293-1301 (1990).
RN [4]; RE0002418.
RX PUBMED: 1986383.
RA DeMarzo A. M., Beck C. A., Onate S. A., Edwards D. P.
RT Dimerization of mammalian progesterone receptors occurs in the absence of DNA and is related to the release of the 90-kDa heat shock protein
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:72-76 (1991).
RN [5]; RE0003737.
RX PUBMED: 3283939.
RA Evans R. M.
RT The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily
RL Science 240:889-895 (1988).
RN [6]; RE0003738.
RX PUBMED: 1587864.
RA Meyer M.-E., Quirin-Stricker C., Lerouge T., Bocqel M.-T., Gronemeyer H.
RT A limiting factor mediates the differential activation of promoters by the human progesterone receptor isoforms
RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:10882-10887 (1992).
RN [7]; RE0003739.
RX PUBMED: 1518826.
RA Rehberger P., Rexin M., Gehring U.
RT Heterotetrameric structure of the human progesterone receptor
RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8001-8005 (1992).
RN [8]; RE0003740.
RX PUBMED: 1312348.
RA Edwards D. P., Estes P. A., Fadok V. A., Bona B. J., Onate S., Nordeen S. K., Welch W. J.
RT Heat shock alters the composition of the heteromeric steroid receptor complexes and enhances receptor activity in vivo
RL Biochemistry 31:2482-2491 (1992).
RN [9]; RE0003745.
RX PUBMED: 3551956.
RA Misrahi M., Atger M., D'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guichon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E.
RT Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem
RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 143:740-748 (1987).
RN [10]; RE0003750.
RX PUBMED: 1730721.
RA Shemshedini L., Ji J., Brou C., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H.
RT In vivo acticity of the transcription activation functions of the progesterone receptor
RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:1834-1839 (1992).
RN [11]; RE0013625.
RX PUBMED: 10219237.
RA Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee.
RT A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily
RL Cell 97:161-163 (1999).
RN [12]; RE0016449.
RX PUBMED: 10428842.
RA Hong H., Yang L., Stallcup M. R.
RT Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3
RL J. Biol. Chem. 274:22618-22626 (1999).
RN [13]; RE0030408.
RX PUBMED: 12771131.
RA Agoulnik I. U., Krause W. C., Bingman W. E. 3rd, Rahman H. T., Amrikachi M., Ayala G. E., Weigel N. L.
RT Repressors of androgen and progesterone receptor action.
RL J. Biol. Chem. 278:31136-48 (2003).
RN [14]; RE0044354.
RX PUBMED: 11773445.
RA Christian M., Pohnke Y., Kempf R., Gellersen B., Brosens J. J.
RT Functional association of PR and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta isoforms: promoter-dependent cooperation between PR-B and liver-enriched inhibitory protein, or liver-enriched activatory protein and PR-A in human endometrial stromal cells
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 16:141-54 (2002).
RN [15]; RE0047476.
RX PUBMED: 12101239.
RA Wardell S. E., Boonyaratanakornkit V., Adelman J. S., Aronheim A., Edwards D. P.
RT Jun dimerization protein 2 functions as a progesterone receptor N-terminal domain coactivator.
RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:5451-5466 (2002).
RN [16]; RE0047660.
RX PUBMED: 12727880.
RA Wiper-Bergeron N., Wu D., Pope L., Schild-Poulter C., Hache R. J.
RT Stimulation of preadipocyte differentiation by steroid through targeting of an HDAC1 complex.
RL EMBO J. 22:2135-2145 (2003).
RN [17]; RE0047842.
RX PUBMED: 15668243.
RA Dong X., Shylnova O., Challis J. R., Lye S. J.
RT Identification and characterization of the protein-associated splicing factor as a negative co-regulator of the progesterone receptor.
RL J. Biol. Chem. 280:13329-13340 (2005).
RN [18]; RE0051005.
RX PUBMED: 16109739.
RA Ma Y., Katiyar P., Jones L. P., Fan S., Zhang Y., Furth P. A., Rosen E. M.
RT The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 regulates progesterone receptor signaling in mammary epithelial cells.
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 20:14-34 (2006).
RN [19]; RE0054750.
RX PUBMED: 15486045.
RA Skildum A., Faivre E., Lange C. A.
RT Progesterone receptors induce cell cycle progression via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases.
RL Mol. Endocrinol. 19:327-339 (2005).
XX
//


PF02161; Progesterone receptor. FT 264 745
PF00478; IMP dehydrogenase / GMP reductase domai. FT 564 635
SM00399; c4gold. FT 564 639
PS51030; NUCLEAR_REC_DBD_2. FT 565 640
PF00105; Zinc finger, C4 type (two domains). FT 720 884
SM00430; holi. FT 723 908
PF00104; Ligand-binding domain of nuclear hormon. FT 904 918
AF-2 domain (transactivation activity) [12].
XX SF alternative promoter usage and, concomitantly, alternative translation initiation gives rise to isoform A T01661 [2]; SF dimerization and nuclear translocation is inhibited by hsp90 [4]; XX FF activator or repressor in response to progesterone; FF both PR isoforms exhibit different promoter specificity [2]; XX IN T08740 batf3; rat, Rattus norvegicus. IN T18805 batf3; human, Homo sapiens. IN T04074 brca1; human, Homo sapiens. IN T06595 C/EBPbeta-FL; human, Homo sapiens. IN T06596 C/EBPbeta-LIP; human, Homo sapiens. IN T01487 cyclinA; human, Homo sapiens. IN T02776 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens. IN T09944 DAX1; human, Homo sapiens. IN T00992 Hsp90; human, Homo sapiens. IN T08741 jdp2; rat, Rattus norvegicus. IN T19032 jdp2; human, Homo sapiens. IN T01661 PR A; human, Homo sapiens. IN T00696 PR B; human, Homo sapiens. IN T08891 PSF-isoform1; human, Homo sapiens. IN T08171 PSF; human, Homo sapiens. IN T21552 SRC-1; Mammalia. IN T02121 TAFII110; fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster. XX MX M00960 V$PR_Q2. MX M03799 V$PR_Q6. XX BS R00973. BS R00974. BS R00975. BS R00976. BS R00978. BS R40171. BS R40172. BS R40173. BS R66028. BS R71596. BS R71599. BS R14315. BS R14316. BS R12328. BS R12329. BS R39279. BS R34883. BS R23811. BS R71581. BS R71583. BS R57486. BS R57499. BS R57502. BS R57508. BS R02234. BS R29385. BS R57260. BS R34881. XX DR TRANSPATH: MO000019617. DR TRANSCOMPEL: C00603. DR PATHODB: MT010691. DR EMBL: M15716; HSPGRR. DR EMBL: X51730; HSPREC. DR UniProtKB: P06401-1; XX RN [1]; RE0000379. RX PUBMED: 3416833. RA Hecht A., Berkenstam A., Stroemstedt P.-E., Gustafsson J.-A., Sippel A. E. RT A progesterone responsive element maps to the far upstream steroid DNase hypersensitive site of chicken lysozyme chromatin RL EMBO J. 7:2063-2073 (1988). RN [2]; RE0000463. RX PUBMED: 2328727. RA Kastner P., Krust A., Turcotte B., Stropp U., Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P. RT Two distinct estrogen-regulated promoters generate transcripts encoding the two functionally different human progesterone receptor forms A and B RL EMBO J. 9:1603-1614 (1990). RN [3]; RE0001752. RX PUBMED: 2172797. RA Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. RT Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model RL Mol. Endocrinol. 4:1293-1301 (1990). RN [4]; RE0002418. RX PUBMED: 1986383. RA DeMarzo A. M., Beck C. A., Onate S. A., Edwards D. P. RT Dimerization of mammalian progesterone receptors occurs in the absence of DNA and is related to the release of the 90-kDa heat shock protein RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:72-76 (1991). RN [5]; RE0003737. RX PUBMED: 3283939. RA Evans R. M. RT The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily RL Science 240:889-895 (1988). RN [6]; RE0003738. RX PUBMED: 1587864. RA Meyer M.-E., Quirin-Stricker C., Lerouge T., Bocqel M.-T., Gronemeyer H. RT A limiting factor mediates the differential activation of promoters by the human progesterone receptor isoforms RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:10882-10887 (1992). RN [7]; RE0003739. RX PUBMED: 1518826. RA Rehberger P., Rexin M., Gehring U. RT Heterotetrameric structure of the human progesterone receptor RL Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8001-8005 (1992). RN [8]; RE0003740. RX PUBMED: 1312348. RA Edwards D. P., Estes P. A., Fadok V. A., Bona B. J., Onate S., Nordeen S. K., Welch W. J. RT Heat shock alters the composition of the heteromeric steroid receptor complexes and enhances receptor activity in vivo RL Biochemistry 31:2482-2491 (1992). RN [9]; RE0003745. RX PUBMED: 3551956. RA Misrahi M., Atger M., D'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guichon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E. RT Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem RL Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 143:740-748 (1987). RN [10]; RE0003750. RX PUBMED: 1730721. RA Shemshedini L., Ji J., Brou C., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. RT In vivo acticity of the transcription activation functions of the progesterone receptor RL J. Biol. Chem. 267:1834-1839 (1992). RN [11]; RE0013625. RX PUBMED: 10219237. RA Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee. RT A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily RL Cell 97:161-163 (1999). RN [12]; RE0016449. RX PUBMED: 10428842. RA Hong H., Yang L., Stallcup M. R. RT Hormone-independent transcriptional activation and coactivator binding by novel orphan nuclear receptor ERR3 RL J. Biol. Chem. 274:22618-22626 (1999). RN [13]; RE0030408. RX PUBMED: 12771131. RA Agoulnik I. U., Krause W. C., Bingman W. E. 3rd, Rahman H. T., Amrikachi M., Ayala G. E., Weigel N. L. RT Repressors of androgen and progesterone receptor action. RL J. Biol. Chem. 278:31136-48 (2003). RN [14]; RE0044354. RX PUBMED: 11773445. RA Christian M., Pohnke Y., Kempf R., Gellersen B., Brosens J. J. RT Functional association of PR and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta isoforms: promoter-dependent cooperation between PR-B and liver-enriched inhibitory protein, or liver-enriched activatory protein and PR-A in human endometrial stromal cells RL Mol. Endocrinol. 16:141-54 (2002). RN [15]; RE0047476. RX PUBMED: 12101239. RA Wardell S. E., Boonyaratanakornkit V., Adelman J. S., Aronheim A., Edwards D. P. RT Jun dimerization protein 2 functions as a progesterone receptor N-terminal domain coactivator. RL Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:5451-5466 (2002). RN [16]; RE0047660. RX PUBMED: 12727880. RA Wiper-Bergeron N., Wu D., Pope L., Schild-Poulter C., Hache R. J. RT Stimulation of preadipocyte differentiation by steroid through targeting of an HDAC1 complex. RL EMBO J. 22:2135-2145 (2003). RN [17]; RE0047842. RX PUBMED: 15668243. RA Dong X., Shylnova O., Challis J. R., Lye S. J. RT Identification and characterization of the protein-associated splicing factor as a negative co-regulator of the progesterone receptor. RL J. Biol. Chem. 280:13329-13340 (2005). RN [18]; RE0051005. RX PUBMED: 16109739. RA Ma Y., Katiyar P., Jones L. P., Fan S., Zhang Y., Furth P. A., Rosen E. M. RT The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 regulates progesterone receptor signaling in mammary epithelial cells. RL Mol. Endocrinol. 20:14-34 (2006). RN [19]; RE0054750. RX PUBMED: 15486045. RA Skildum A., Faivre E., Lange C. A. RT Progesterone receptors induce cell cycle progression via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. RL Mol. Endocrinol. 19:327-339 (2005). XX //